- Hybrid Sleep is another power state a modern Windows computer can use to resume work faster than a normal shutdown.
- Hybrid Sleep is a combination of hibernation and sleep modes and borrows both advantages and disadvantages from these modes.
- Learn how Hybrid Sleep works in Windows and how you can enable this mode.

Ask someone what’s the difference between Hibernation, Sleep, and Fast Startup and they’ll look at you in a certain way. Now ask them about Hybrid Sleep and you may discover a side of their personality they thought was well hidden from sight.
But the Windows sleep modes don’t have to be that complicated. You don’t even need to deal with them, but if you want to control precisely how your computer turns off and how it resumes work then it does help to know what Hybrid Sleep is and how it works.
Let’s get going.
What is Hybrid Sleep?
Hybrid Sleep in Windows is a combination of the regular Sleep mode and Hibernation. When a computer is put to hybrid sleep it writes the current memory contents to a file on the primary system disk, then puts the hardware in a very low power mode.
Only key components are powered in Hybrid Sleep, the same as during the Sleep mode. The RAM keeps refreshing to keep the data intact, while the system looks for user input from the keyboard, mouse, or even the NIC card, depending on how you’ve configured your system.
If a power outage occurs the system will resume and copy the hibernation file data to RAM, exactly as it happens when your resume from hibernation. Nothing is lost, but it will take a bit longer to resume.
If you press a key or move the mouse the system will resume in a few seconds, exactly as it happens from normal Sleep, though not blazing fast as on a Mac. There’s no need to read the hibernation file.
You can view Hybrid Sleep as a Sleep + Hibernate power mode. Don’t confuse it with Fast Startup, which also uses a bit of hibernation “magic”, but in the end powers off the computer.
One interesting difference is what happens if you set your Windows power plan to Hibernate after a longer interval of Sleep.
- When Hybrid Sleep is active the system will just turn off, as the data is already saved to the hibernation file.
- When Hybrid Sleep is turned off the system will resume full power, the monitor will turn on, then hibernation begins writing the RAM contents to the disk, and turning the system off at the end.
Putting a computer into Hybrid Sleep will take just as long as Hibernation, but will resume faster when turned on again. You’ll still need enough space on the main partition for the hibernation file. Also, power consumption in Hybrid Sleep is just as high as in Sleep compared to hibernation.
You could say that Hybrid Sleep takes the worse parts of Sleep and Hibernation, and you would be almost correct if it wasn’t for the ability to resume work in case of a power failure, something only hibernation can do.
How to Enable Hybrid Sleep in a Windows Power Plan?
First, if you’re using a desktop and you haven’t changed the Hybrid Sleep settings before then most likely this standby mode is already enabled on your PC.
On laptops, hybrid mode is disabled by default, as it consumes more power than hibernation. Plus, the laptop battery can deal with power outages and there’s no risk of losing the current system state.
That doesn’t mean you wouldn’t want to use Hybrid Sleep on a laptop. Just be aware of the higher power consumption, similar to the regular Sleep mode.
Let’s see how you modify the Hybrid Sleep settings in Windows.
This guide works for both Windows 10 and Windows 11.
1. Open the Start menu and type Control Panel then launch the first option presented to you.
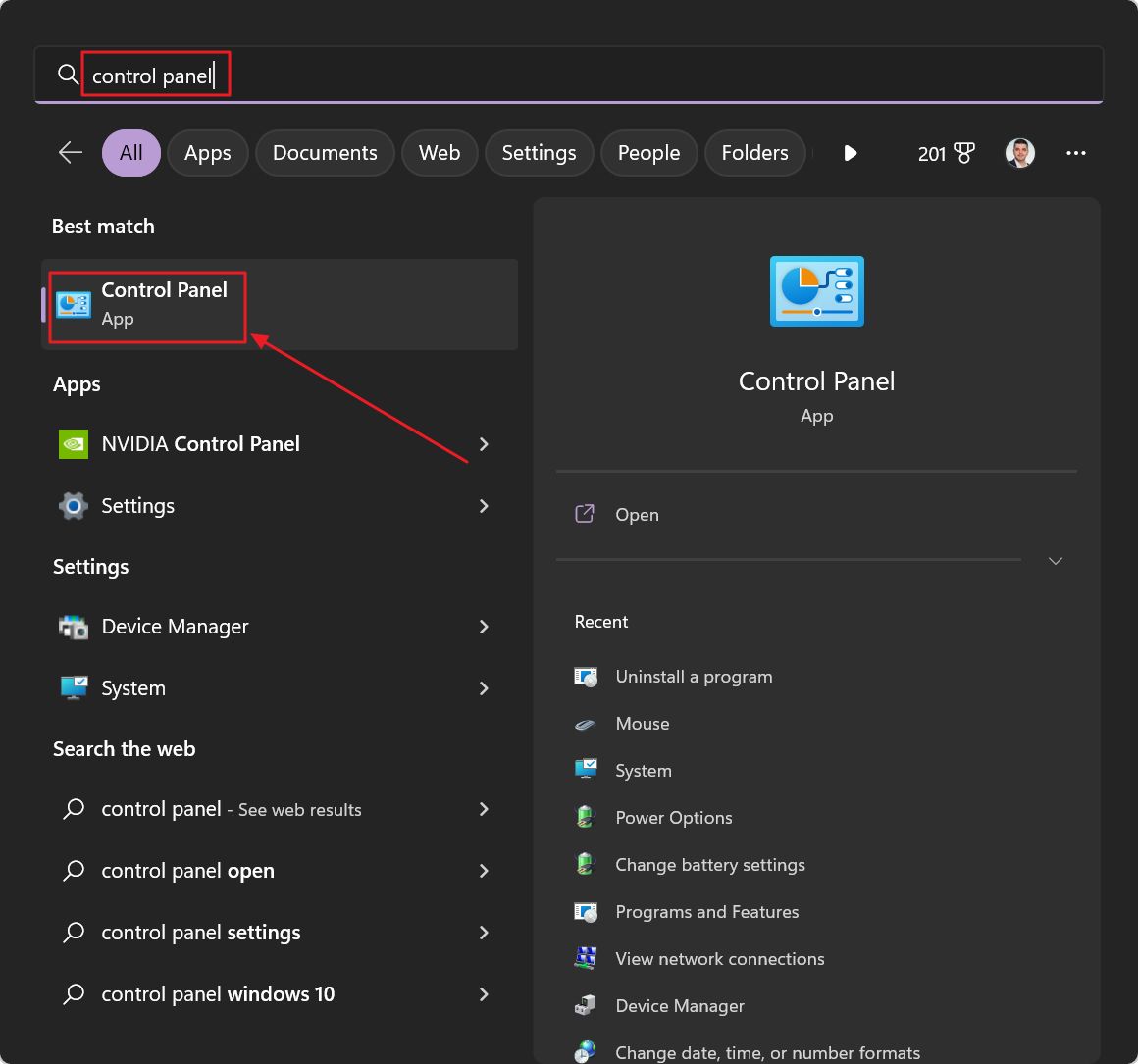
2. Select the Hardware and Sound section. You can click on the light blue outline when you hover over it or on the green section title.
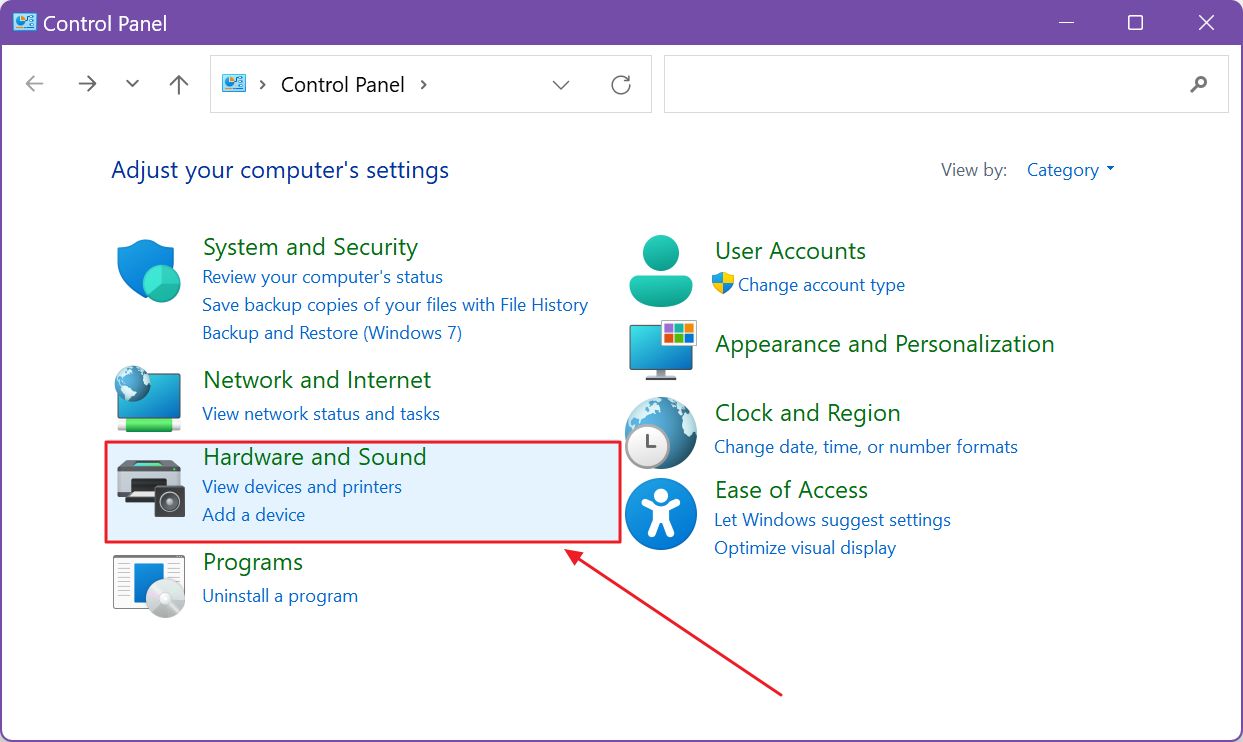
3. Click on the Edit power plan link on the new page.
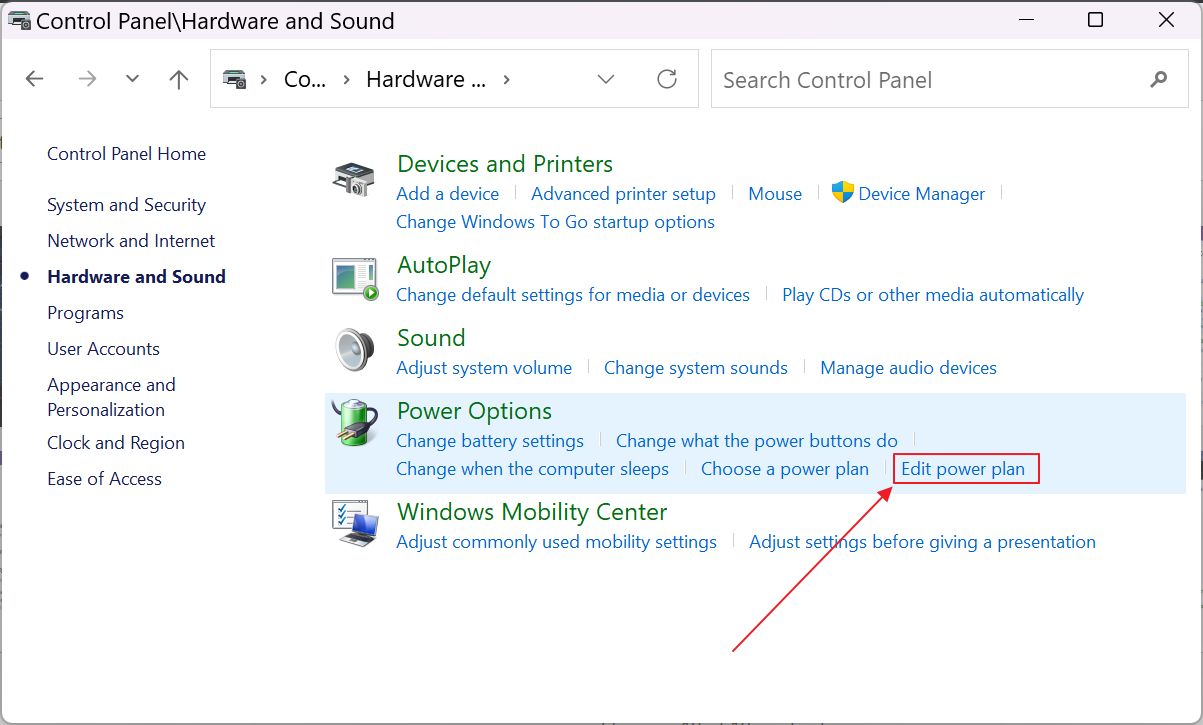
4. The Change settings for the plan: current plan window will open. Click on the Change advanced power settings blue link.
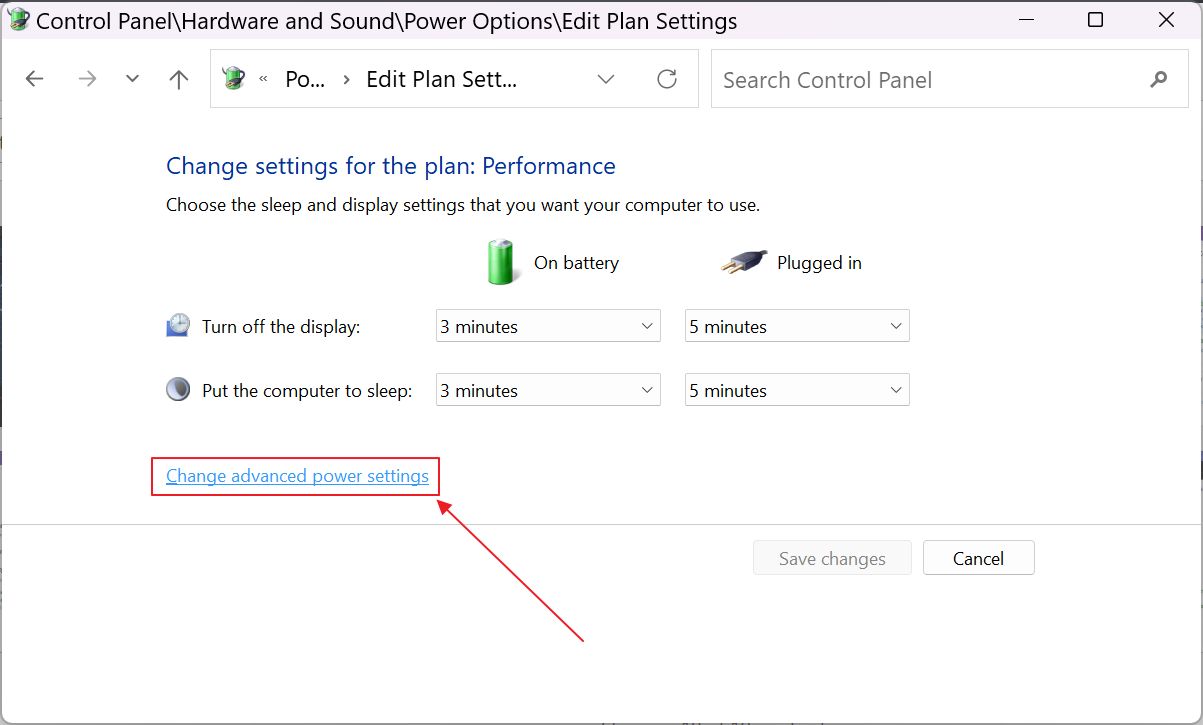
5. A new popup will show up. All power plan options will be contracted, so navigate to Sleep > Allow hybrid sleep and modify the setting to On.
Confirm with OK or Apply, both found at the bottom.
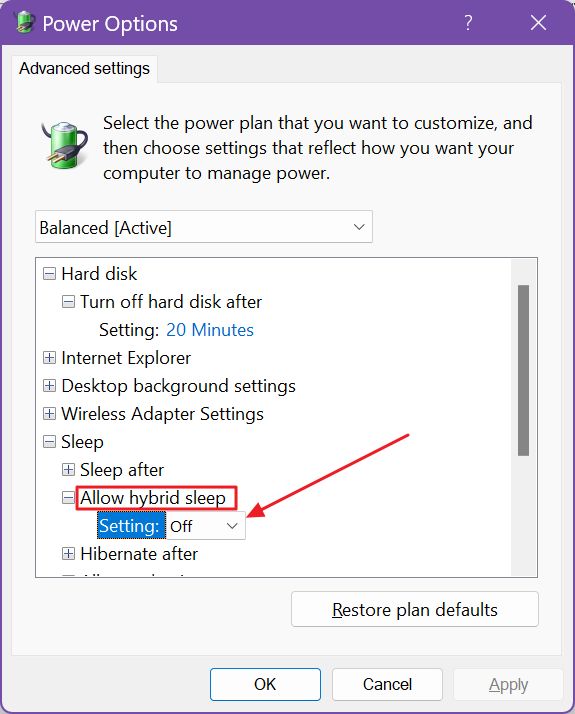
If you’re using more than one Power Plan, and use them regularly, you need to enable Hybrid Sleep for each of them.
On some devices, Hybrid Sleep may not even be available, depending on hardware support.
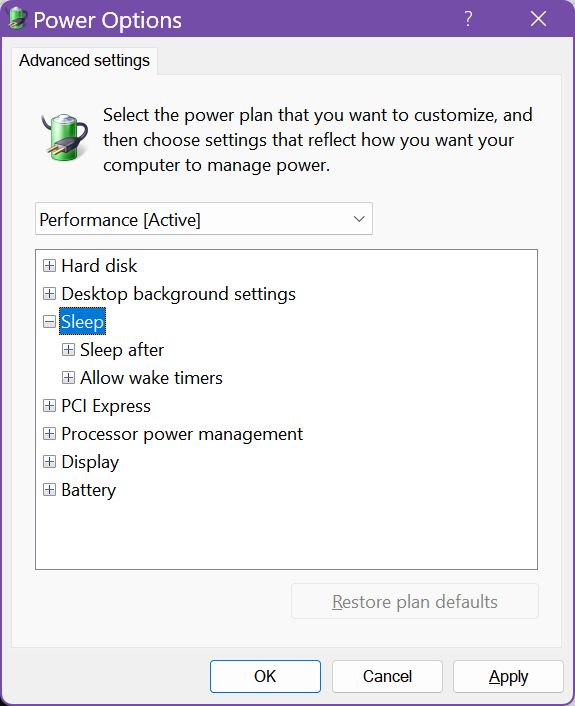
You can select the other power plans installed on your system from the same window. Notice the drop-down list selector at the top of the window. Repeat the steps for each plan, if you want Hybrid Sleep enabled for all of them.
Want to learn more about current power states in Windows? Read about Modern Connected Standby and why I chose to keep it turned off.