- If Antimalware Service Executable shows in Task Manager with high CPU, memory, or disk usage there are a few things you can try to fix.
- Antimalware Service Executable is an essential part of Windows Security and is always running on your computer.
- The best way to remove Antimalware Service Executable is to install a third-party antivirus, as Microsoft Windows Defender will automatically disable itself.

For the past few Windows versions, Microsoft has included antivirus software in their OS as a baseline for computer security. It’s comforting to know that Windows is somewhat protected immediately after you install the OS I guess. It’s something else you don’t need to install and configure.
Microsoft Windows Defender is not the best antivirus, but it’s better than nothing. For me, it’s enough, especially since I’m careful about which websites I access and what files I download.
Anyway, I’m not trying to sell you on the idea of using Microsoft Defender Antivirus (that’s what it’s called in Windows 11 now).
I’m just trying to address the questions regarding the Antimalware Service Executable that’s always running and sometimes causes high CPU, RAM, and Disk usage in Task Manager, significantly slowing down your PC.
CONTENTS
- What is Antimalware Service Executable (msmpeng.exe)? Is it a Virus?
- Why is Antimalware Service Executable Always Running?
- How to Check Antimalware Service Executable Resource Usage
- How to Disable, Stop or Turn Off Antimalware Service Executable?
- How to Fix High CPU, Memory, or Disk Usage?
- Things that Don’t Work If You Try to Remove Antimalware Service Executable
- How to Delete Antimalware Service Executable?
What is Antimalware Service Executable (msmpeng.exe)? Is it a Virus?
The Antimalware Service Executable process is the main Microsoft Defender antivirus background service, and for security reasons, it is always running in the background.
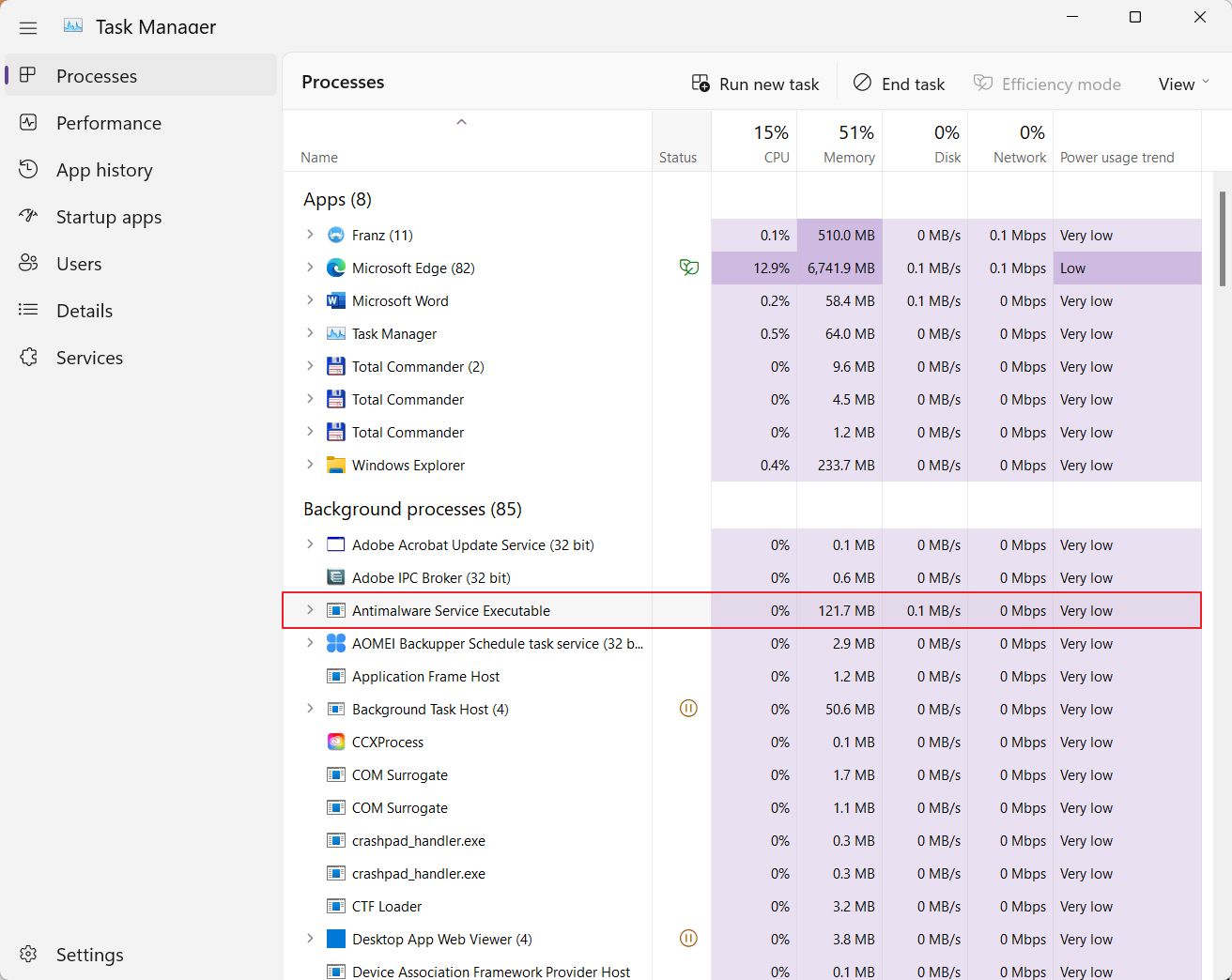
So no, Antimalware Service Executable is not a virus, far from that.
If you open the Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc shortcut) you will see that you can expand the Background processes entry for Antimalware Service Executable. This will reveal it’s part of the Microsoft Defender Antivirus Service.

If you go to the Details tab in Task Manager you will see that the actual file that opens the process is called MsMpEng.exe. This is the Microsoft Defender executable associated with the Antimalware Service Executable.
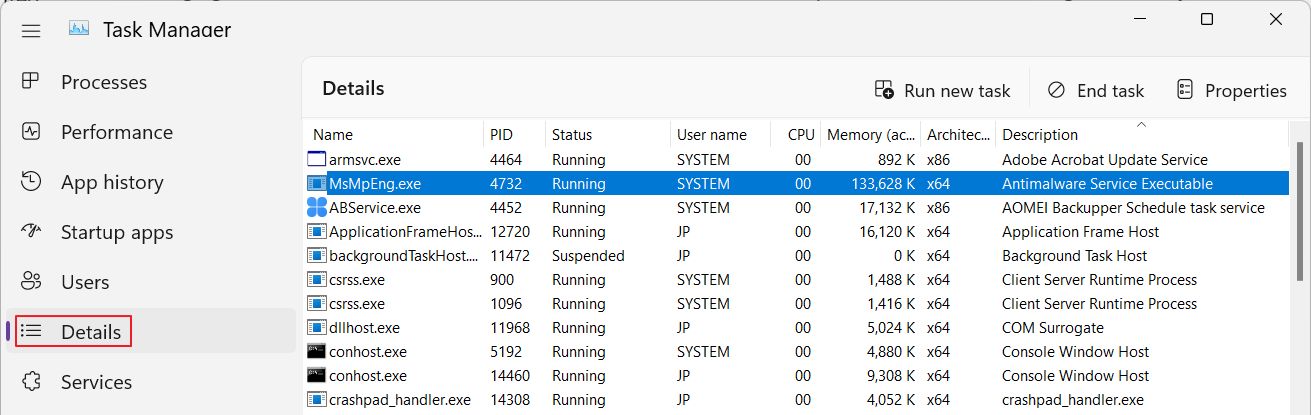
Why is Antimalware Service Executable Always Running?
Among the things this service provides is real-time protection, as it scans all the time the files you access and run (manually or automatically). These files are compared against known virus and threat signatures.
That’s one of the reasons Antimalware Service Executable runs all the time on your computer, launching when the computer starts, even before you login to your account.
How to Check Antimalware Service Executable Resource Usage
Most of the time Antimalware Service Executable takes little to no system resources. It depends on what you’re doing, but the usage can spike when you run a manual or scheduled system scan, when you launch a new program, download a file from the Internet, or when you install something.
Some of these tasks are already resource-heavy, so the Antimalware Service Executable usage will compound.
If you want to check current resource usage:
- Open the Task Manager again (you can use the Ctrl + Shift + Esc shortcut)
- Select the Processes tab.
- In the Background processes section look for the Antimalware Service Executable entry.
- Check CPU, Memory, and Disk columns for instant usage (see this guide if you can’t manage).
How to Disable, Stop or Turn Off Antimalware Service Executable?
You actually can’t stop the Antimalware Service Executable as you normally would in Windows with any running program.
If you install a third-party antivirus Windows will detect it and will automatically disable the Antimalware Service Executable service.
This means trading one background process for another, nothing else. But technically, this is how you remove the Antimalware Service Executable from Windows.
How to Fix High CPU, Memory, or Disk Usage?
If resource usage is high, like in the image below, your computer might feel slower than usual, noise could be higher and, if you’re on a laptop, it will be warmer to the touch, while lasting less on battery.
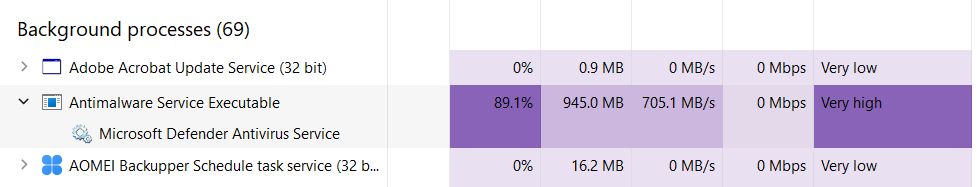
Normally, Antimalware Service Executable resource usage should return to normal after a regular or manual scan ends, and should only occasionally spike when you download files from the Internet or when you install and start programs.
If that doesn’t happen there are a few things you can try to lower usage, beside rebooting your system:
1. Turn Off Real-Time Protection Temporarily from Windows Security
You can only temporarily disable Microsoft Defender’s real-time protection without installing another antivirus. After a while, Windows will reactivate Defender automatically. So, in theory, this could solve high resource usage problems, but those problems would come up again once the service starts up again.
1. Open the Start menu and type Windows Security, then open the first result.
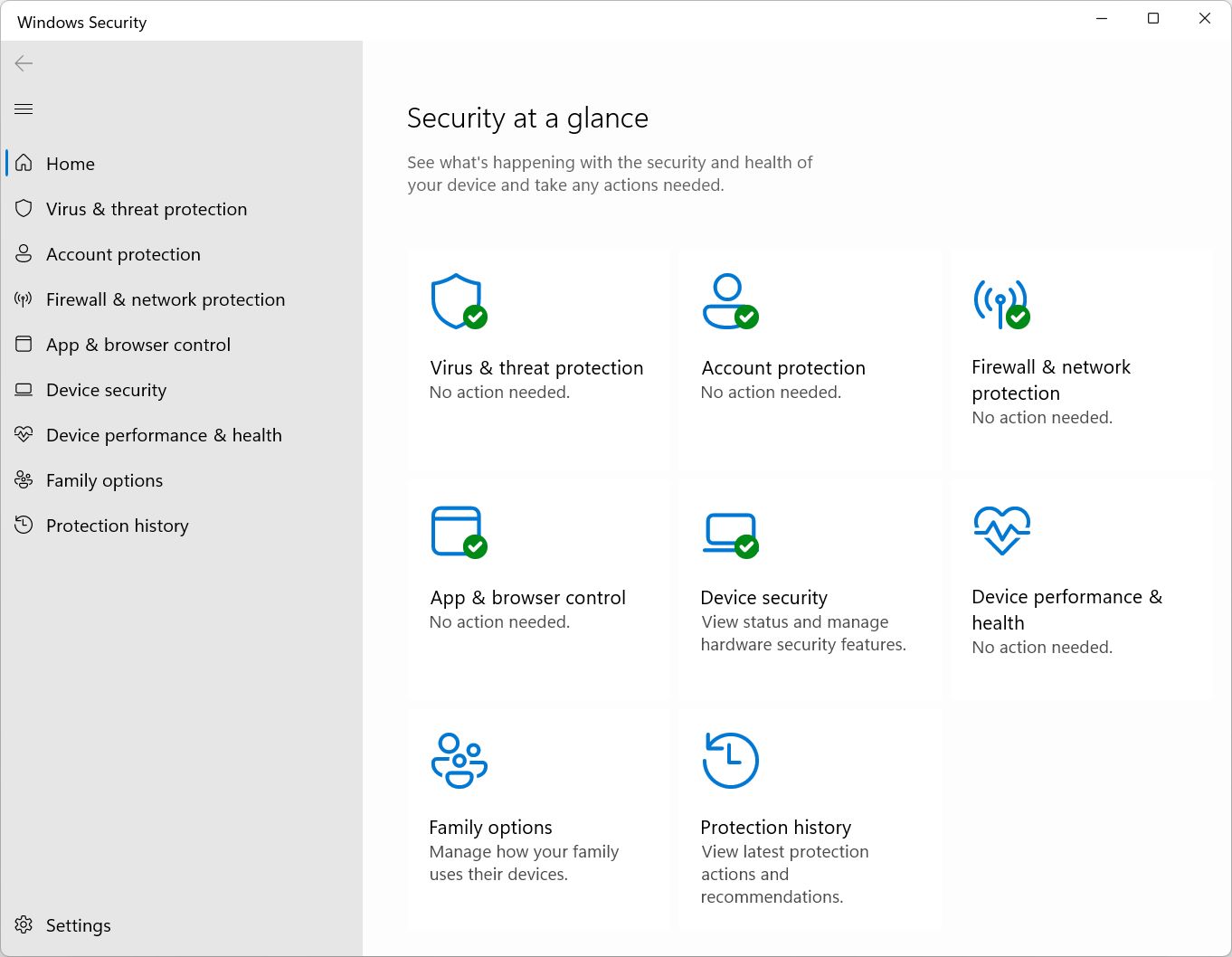
2. Navigate to the Virus & threat protection section from the left side menu.
3. Scroll to Virus & threat protection settings and click on the Manage settings link.
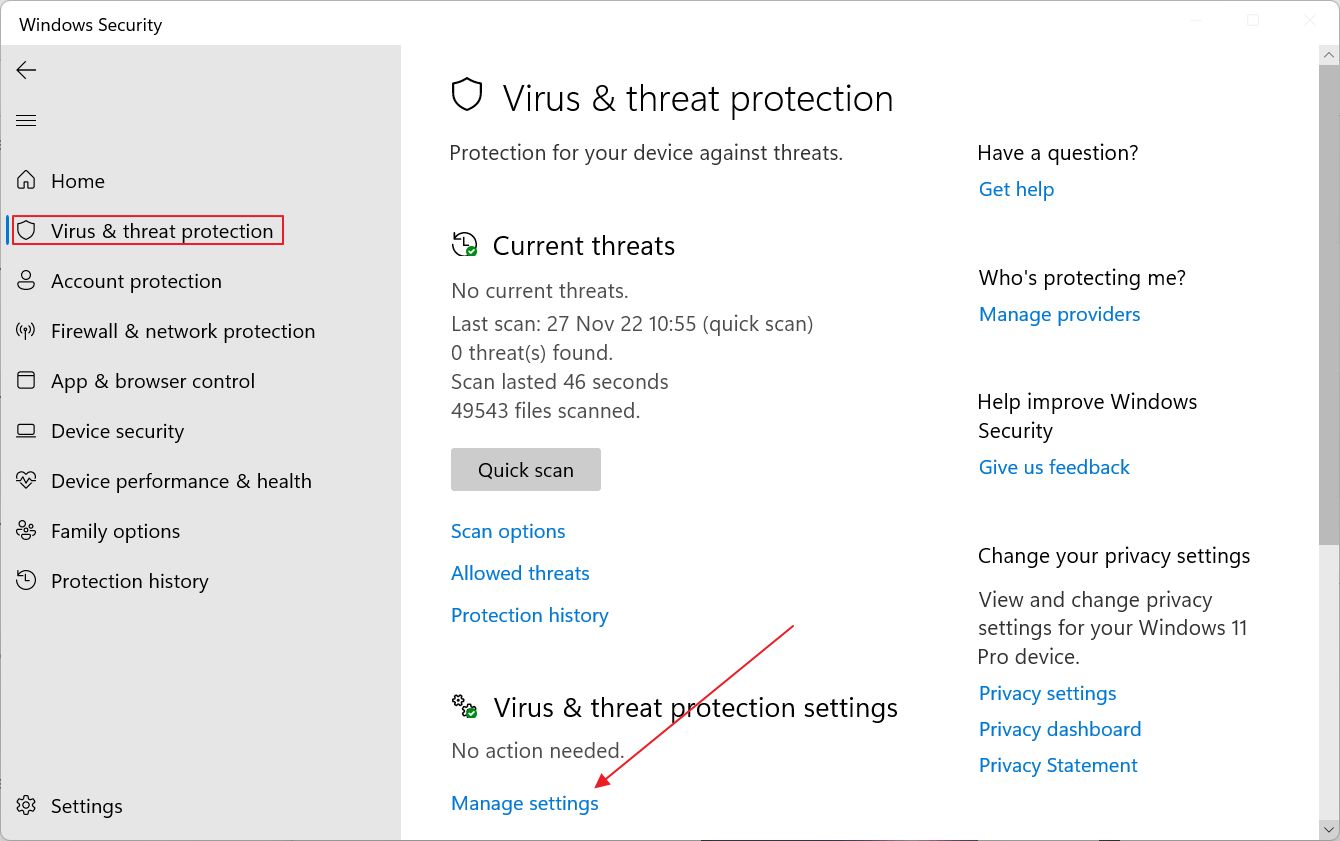
4. The first option in the next page is the Real-time protection toggle. Disable it to stop the background service from scanning everything. As I said, this is only temporary.
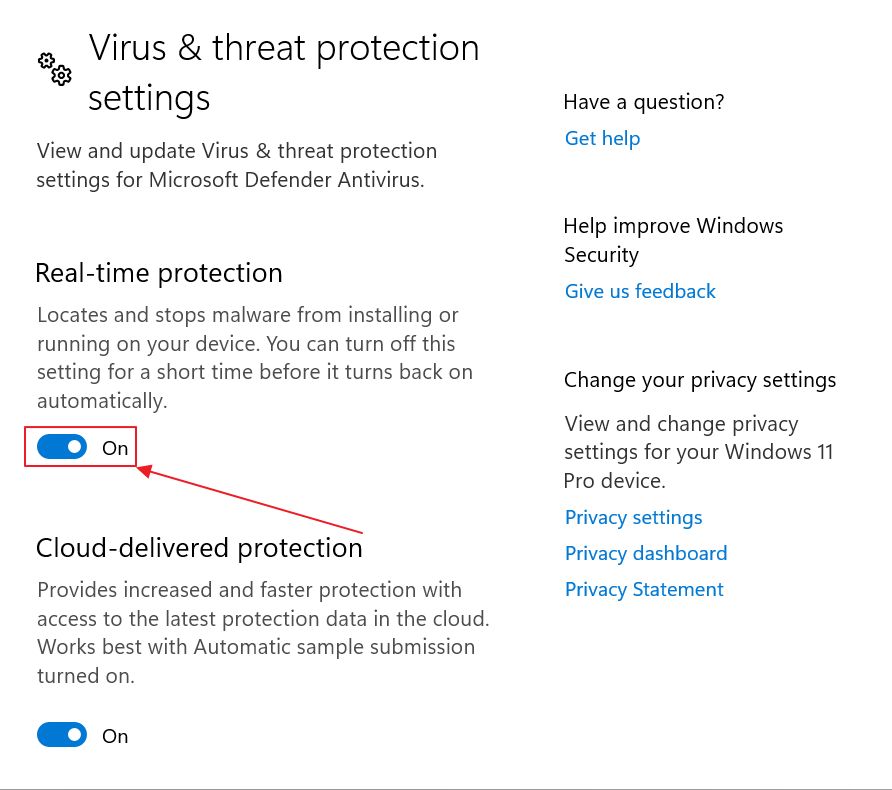
Windows will immediately prompt you with the warning below, so consider yourself warned.
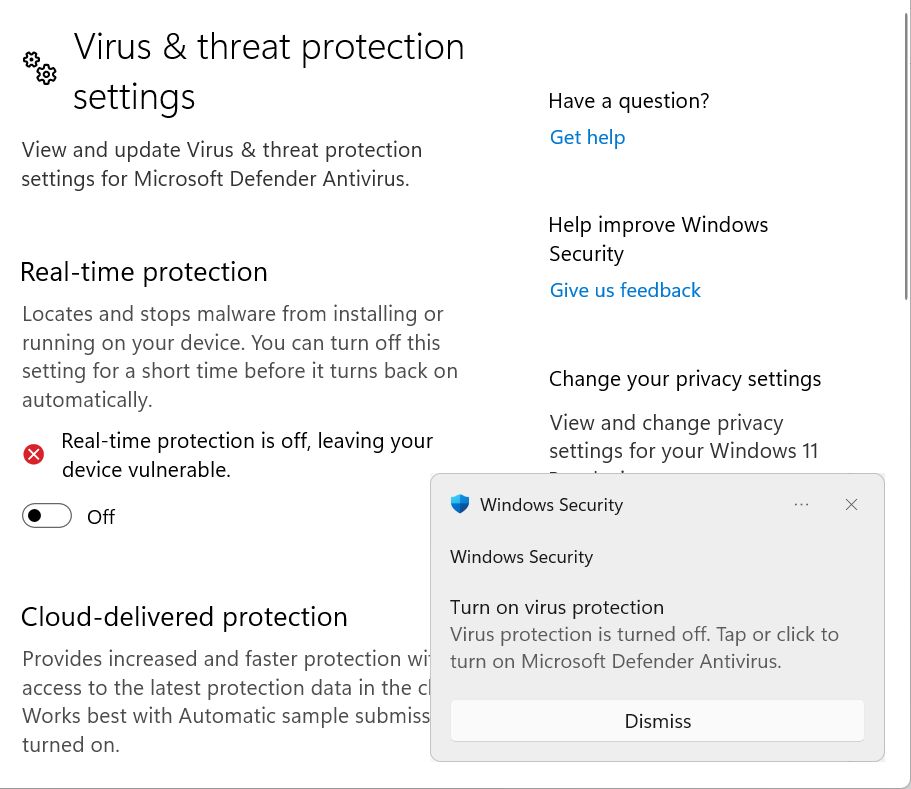
I would only turn off protection if for some reason I can’t install a specific program that I know is safe to use. I can’t think of another reason to disable Microsoft Defender Antivirus without using another antivirus.
Note: the process will still show up in Task Manager, but resource usage should be almost zero on all columns.
2. Cancel the Current Antivirus System Scan
Most of the time high CPU usage caused by Antimalware Service Executable is linked to a system scan. This is very resource intensive, especially when it comes to CPU usage, but will also increase RAM and disk usage at the same time. Basically, only the GPU is left idling, if you’re not using it for something else.
Here’s how to check if a system scan is taking place and how to cancel it:
1. Open the Windows Security once again.
2. Navigate to Virus and threat protection tab.
3. Check the first section, Current threats. If you see Quick scan running…click on the Cancel button to stop the scan.
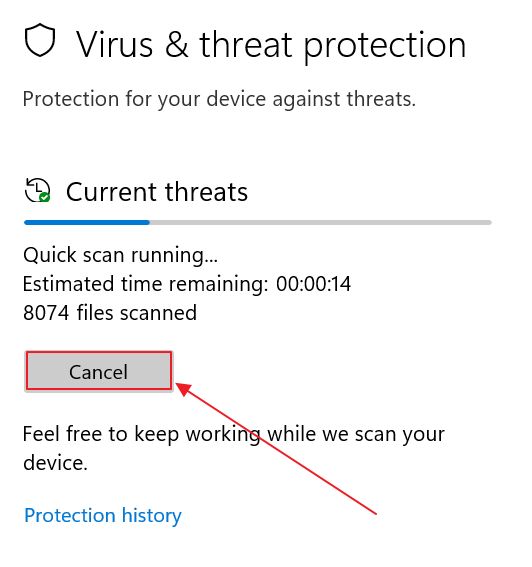
Doing this should drop the high resource usage immediately.
3. Check the Task Scheduler for Scheduled System Scans
The thing is that Windows will run periodic Microsoft Defender scans by using the Task Scheduler. This is where we’re going to look next.
1. Open the Start menu and type Task Scheduler. Select the first result.
2. Navigate the left menu to Task Scheduler Library > Microsoft > Windows > Windows Defender.
3. In the middle pane select the task called Windows Defender Scheduled Scan. Double click to open the task properties.
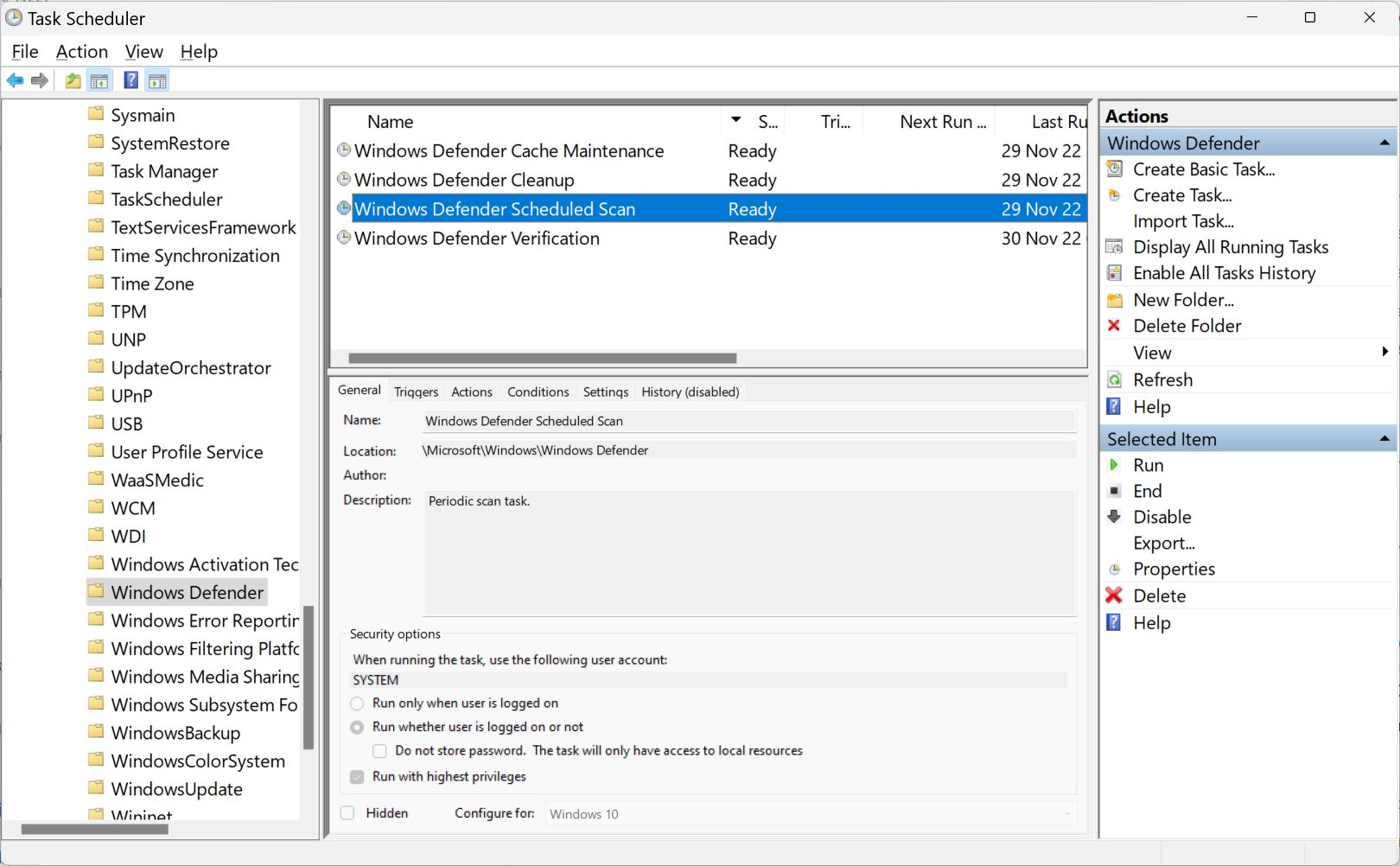
4. Change the following settings:
- General tab – Uncheck Run with highest privileges.
- Triggers – remove the existing schedules or add your own schedule.
- Conditions – uncheck everything.
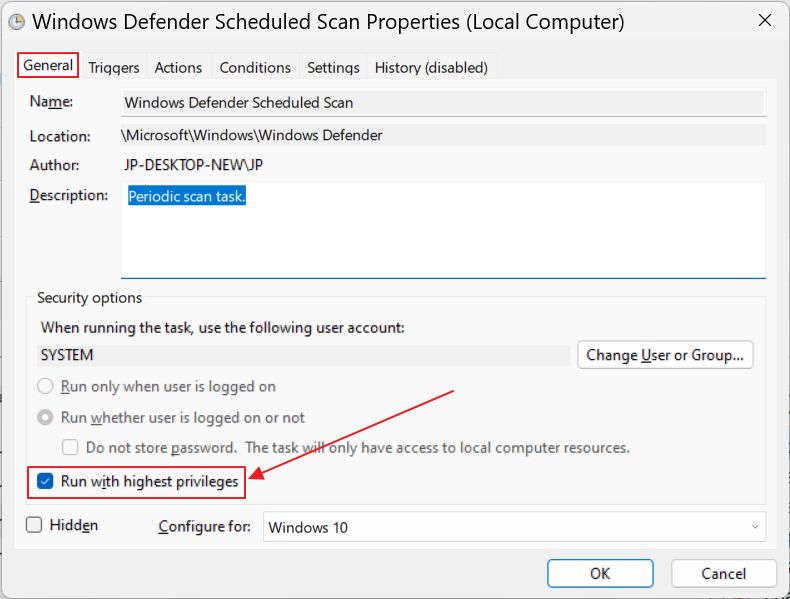
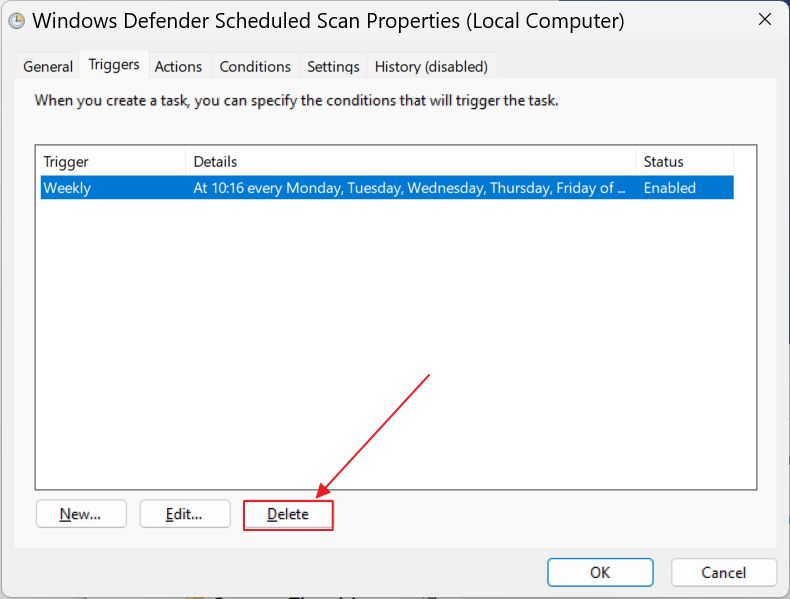
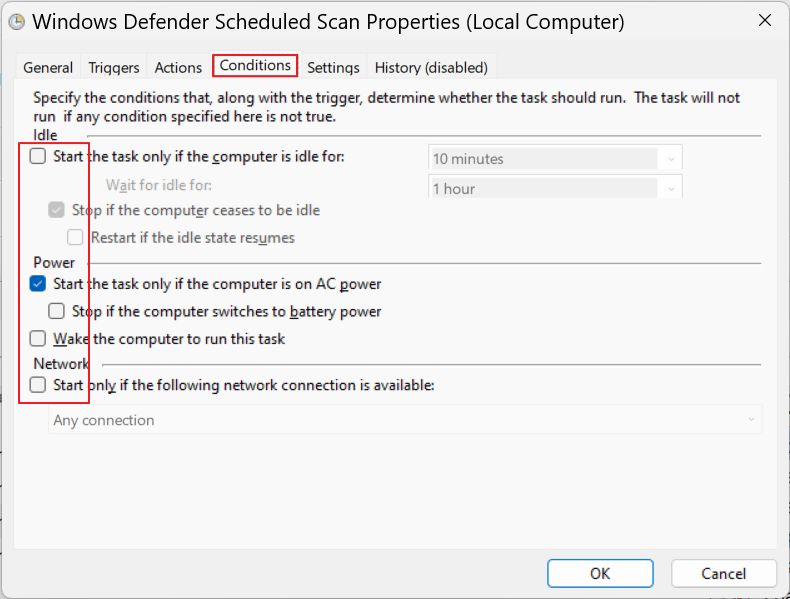
For some reason Microsoft did something to hide the periodic triggers it sets automatically. I know the system is scanned because I’m being notified after each scan in the Action Center. So the triggers exist, but they’re hidden in Task Scheduler. In this case the only option would be to add your own schedule.
Again, I strongly encourage you not to mess with these periodic scans because they will scan files stored on your disk, not just things found in RAM. Periodic scans could detect viruses and other threats, so I wouldn’t remove these scans.
I would probably reschedule them to a time when I know I won’t be running intensive programs on my PC.
4. Add the Windows Defender Folder to the Exclusion List
Another weird thing that can happen, which may increase resource usage is Microsoft Defender scanning itself. Fortunatelly, you can add the program folder to an exception list.
Mind you that viruses which manage to gain access to this folder could compromise Defender, so it’s again something I don’t recommend you do, unless the Antimalware Service Executable causes serious slow downs and nothing else from this article works for you.
1. Open the Windows Security app again.
2. Go go Virus & threat protection.
3. Click on the Manage settings link.
4. Scroll to Exclusions and click on the Add or remove exclusions link. You will need to confirm the next UAC prompt.
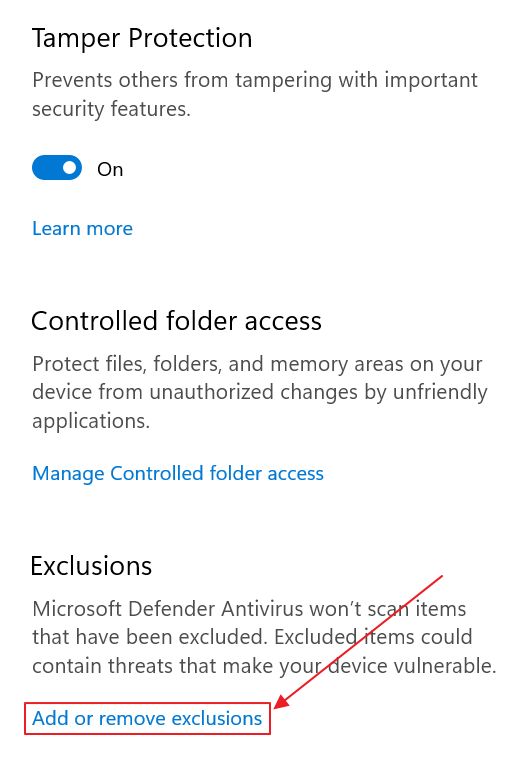
5. In the new page click on the Add an exclusion button and select Folder.
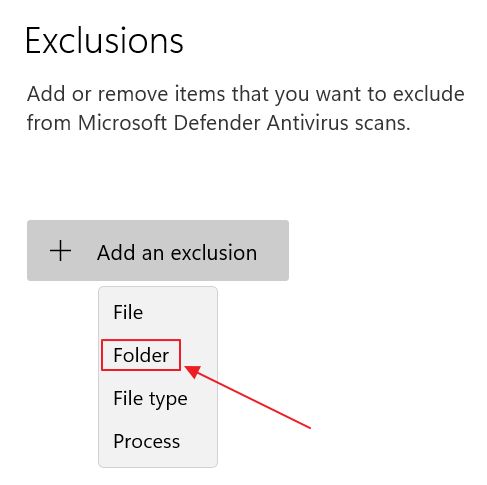
6. Navigate to the following folder:
C:\Program Files\Windows Defender\Confirm with the Select Folder button.
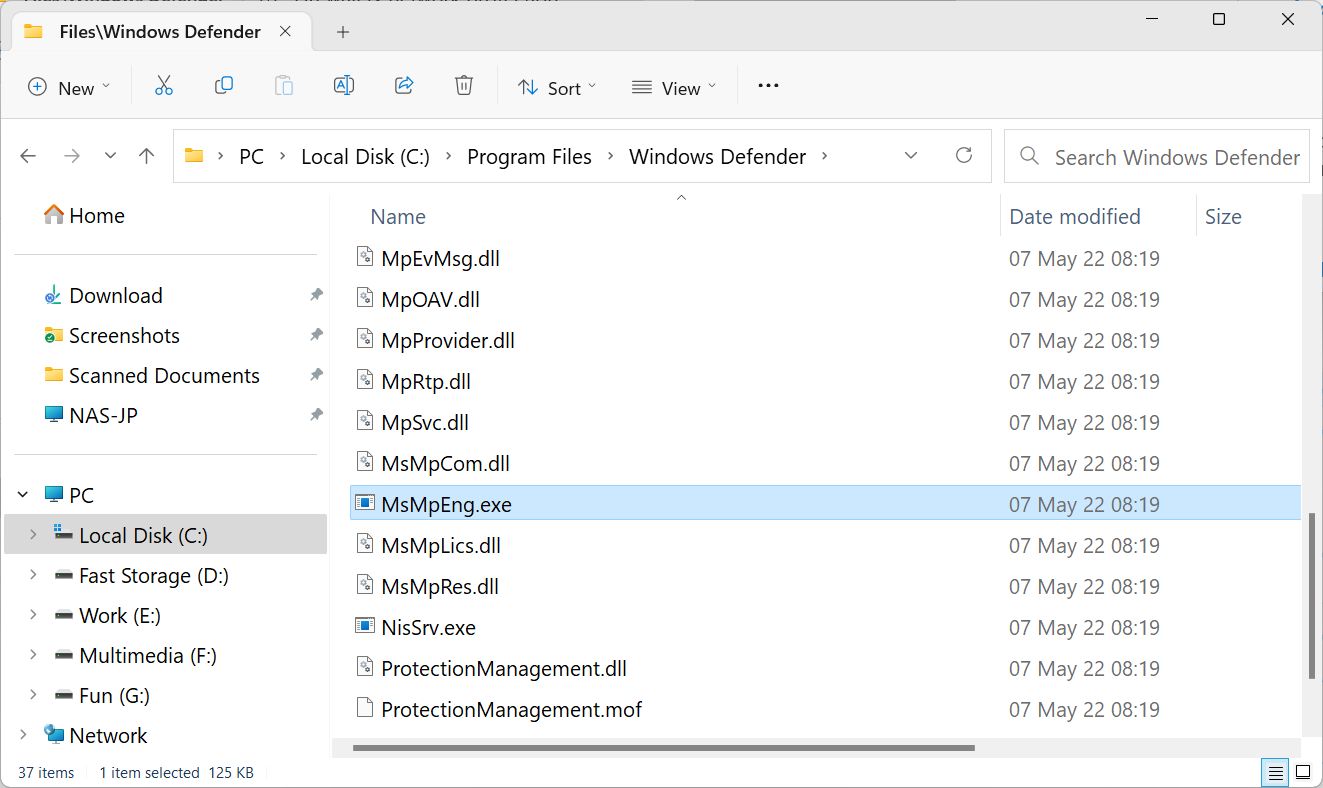
If you browse the contents of the folder in File Explorer you’ll find the MsMpEng.exe executable, the one that launches the Antimalware Service Executable process in the first place.
Things that Don’t Work If You Try to Remove Antimalware Service Executable
I’ve tried a few things I’ve seen mentioned by other websites and I have to say that Microsoft got better at keeping Windows Defender secure from internal and external threats (yeah, users are threats too). None of the guides below worked in Windows 11, but may still work in Windows 10.
1. Disable Windows Defender with a Registry Key is Seen as a Tampering Attempt
You can use the Registry Editor to add a new DWORD 32-bit key called DisableAntiSpyware with the value 1 in:
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender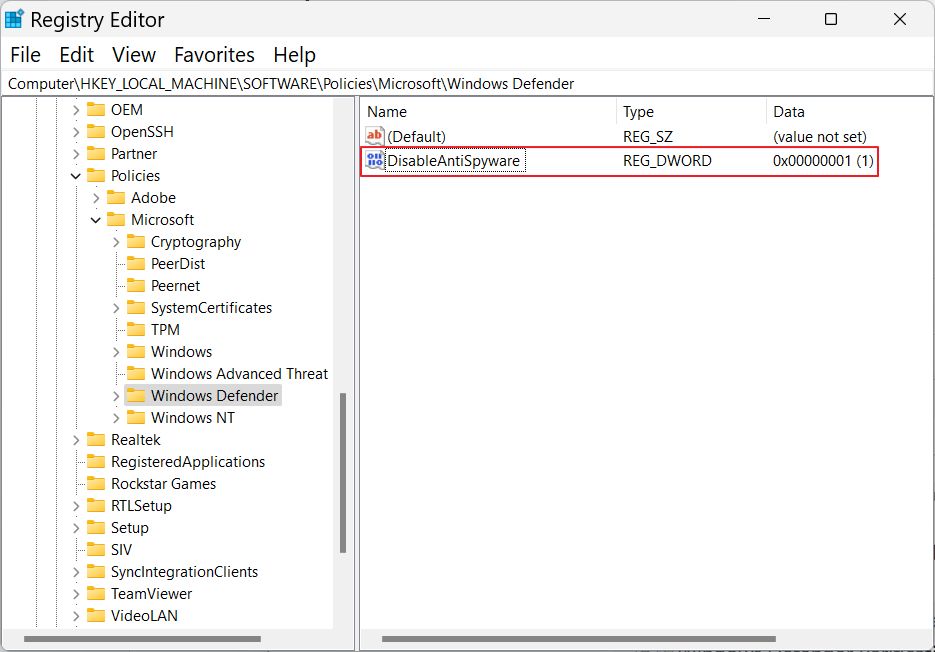
This should disable Microsoft Defender completely, but in a few moments you’ll get a notification that a severe threat was found by a system scan.
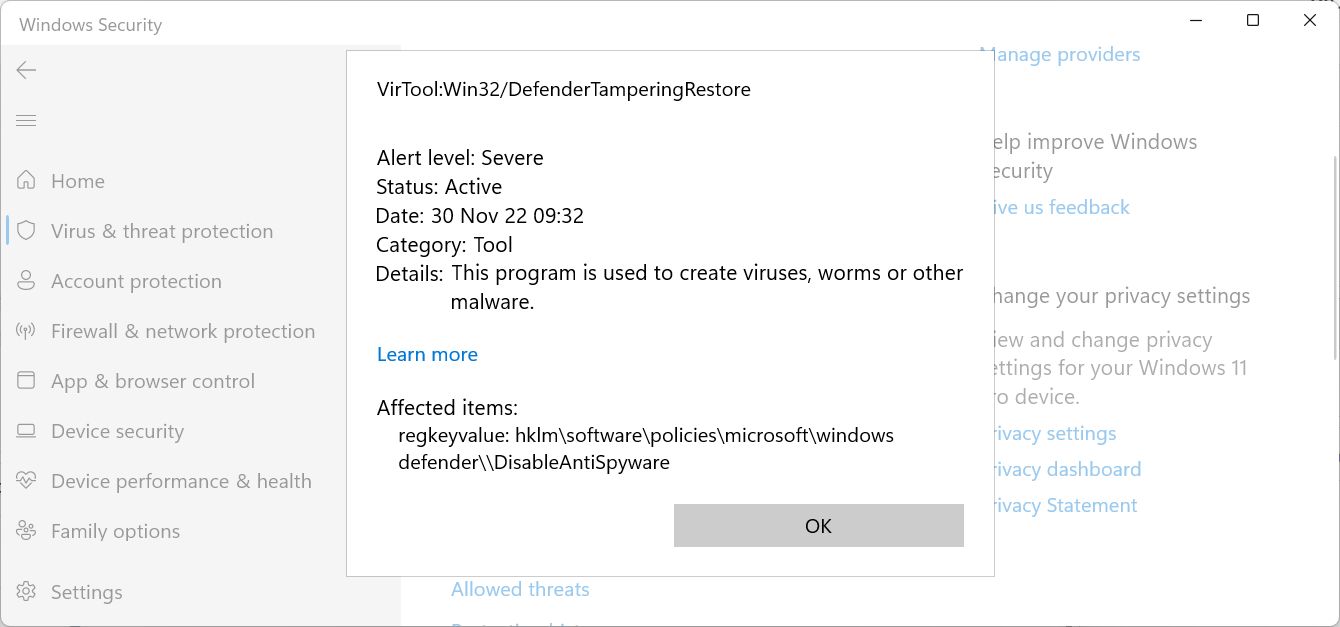
Choosing to remove or quarantine the threat will remove the registry key.
2. You Cannot Stop the Microsoft Defender Antivirus Service
If you type Services in the Start menu you will open the list of currently registered Windows Services. If you scroll, find and double-click the listing called Microsoft Defender Antivirus Service the buttons for Start, Stop, Pause, and Resume are all disabled.
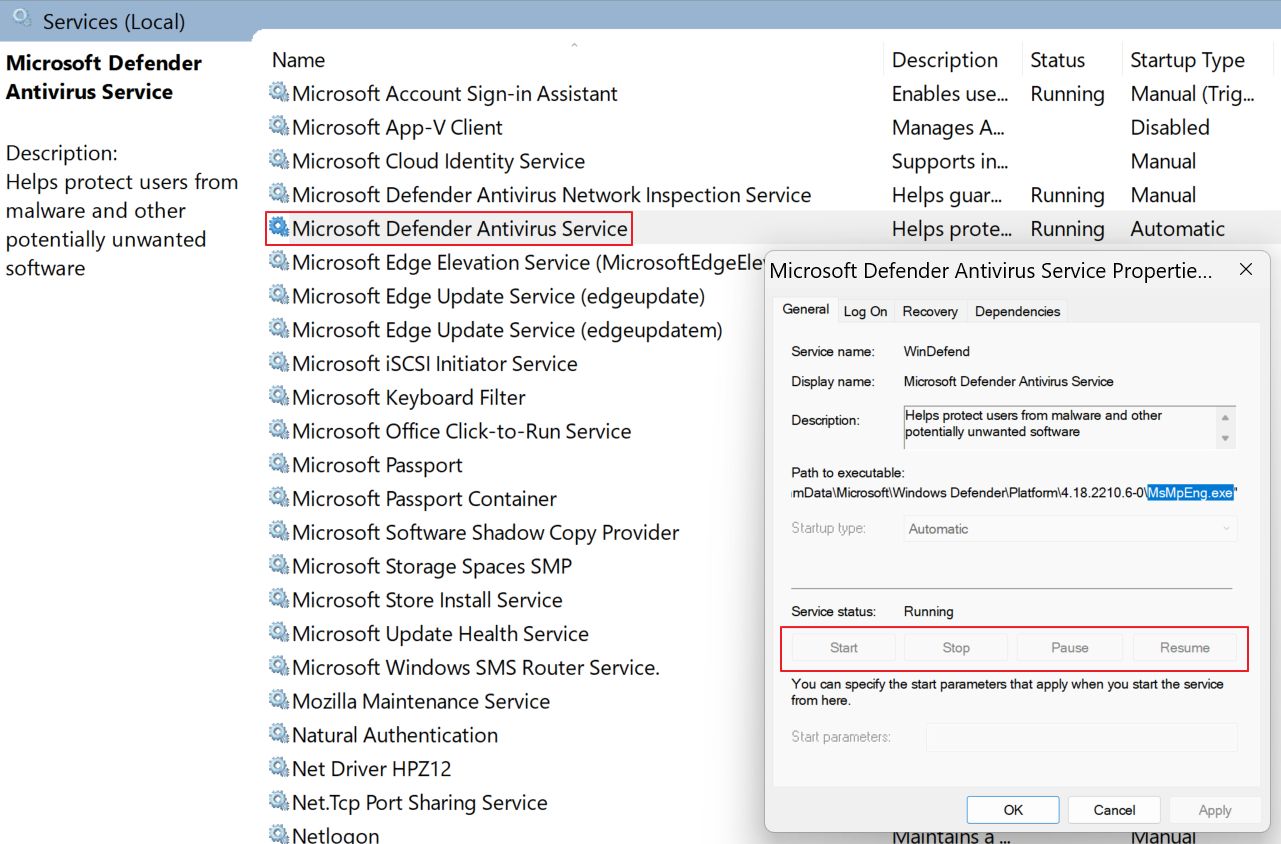
3. You Can’t End Antimalware Service Executable From Task Manager
Most programs and processes listed in Task Manager can by stopped, but that’s not possible with the Antimalware Service Executable.
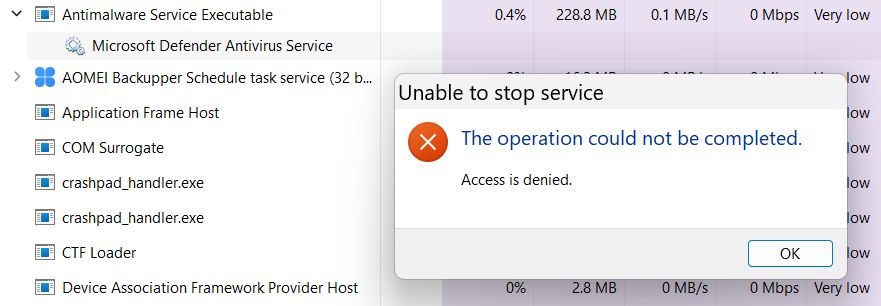
If you right click on the process and select Stop you will immediately get this message, that The operation could not be completed with the reason that Access is denied.
How to Delete Antimalware Service Executable?
You can’t and most likely don’t want to delete Microsoft Windows Defender. It’s an integral part of the Windows operating system.
Installing a third-party antivirus will automatically stop the Antimalware Service Executable and this is the way to go if the process causes problems on your computer.
Did these guides solve the high resource usage caused by the Antimalware Service Executable process? Let me know in the comments.