- Learn how to check RAM memory usage in Windows, how to see which app causes this problem, and what you can do to solve this issue.
- RAM memory used to be a problem until recent years because it wasn’t enough and HDD swapping data was very slow.
- Apps can still eat a lot of memory in Windows, slowing your system down when it fills up too much.
You can find the current total RAM usage in Windows in Task Manager > Performance > Memory. In the Processes tab you will find how much RAM each application is using at one time.
I remember the times when my computer had only 4 MB of RAM. Yes, it’s not a typo. And it was very noisy because hard disk drives got used a lot back then for swapping data when RAM was filled up.
That posed a new problem: an HDD is hundred of times slower than RAM, so when it’s used for swapping (an operation that basically simulates RAM) your PC gets very slow. If you’re used to SSDs then you don’t know what I’m talking about.
RAM stands for Random Access Memory. RAM is known as memory and differs from storage in the sense that program files are stored on your storage drive while instructions and results from program executions are stored in RAM temporarily.
Storage data is permanent. RAM is emptied when your reboot or turn off your computer.
I’ll just say this: HDD swapping feels like your computer is dying and it doesn’t respond to your input.
In modern times RAM is not that much of a problem in Windows. If you have enough RAM it’s never a problem. It’s not faster either if you have twice or more RAM than you actually need. But that’s for another time.
In this article, we’re going to see how you can check RAM usage in Windows, how to see which program is eating RAM like it is a continental breakfast, plus a few tricks to fix some high memory usage-related problems.
CONTENTS
Check Total Installed RAM, Currently Used, and Free RAM
First, let’s see how we check how much memory is installed on your PC. For this, we are going to use Task Manager, one of the cool free utilities bundled with Windows since the beginning of time.
1. Open the Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc.
2. If it’s the first time, the app will look like the image below. Click on More details to open a detailed view in Task Manager. This is where the magic happens.
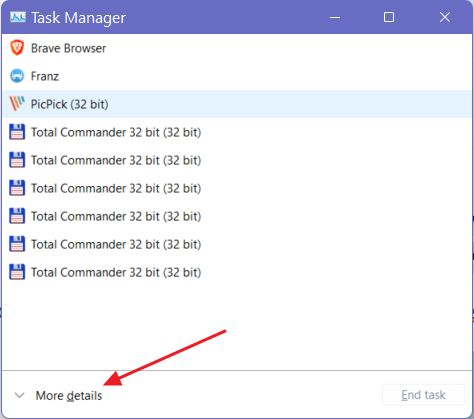
3. Select the completely unintuitive Performance tab.
4. Click on the Memory tab on the left column, even if these don’t look like buttons.
You can stop right before this step and just check the stats displayed under the header. Windows lists used memory in gigabytes, total RAM installed and percentage of RAM used. We’re not going to stop, though.
5. Once you click on Memory, the right panel will refresh and display a nice graph with memory usage in the past 60 seconds. On top, there are two numbers, almost equal, but not quite, due to rounding and to the fact a small amount is reserved by the system. So no, nobody stole your bytes.
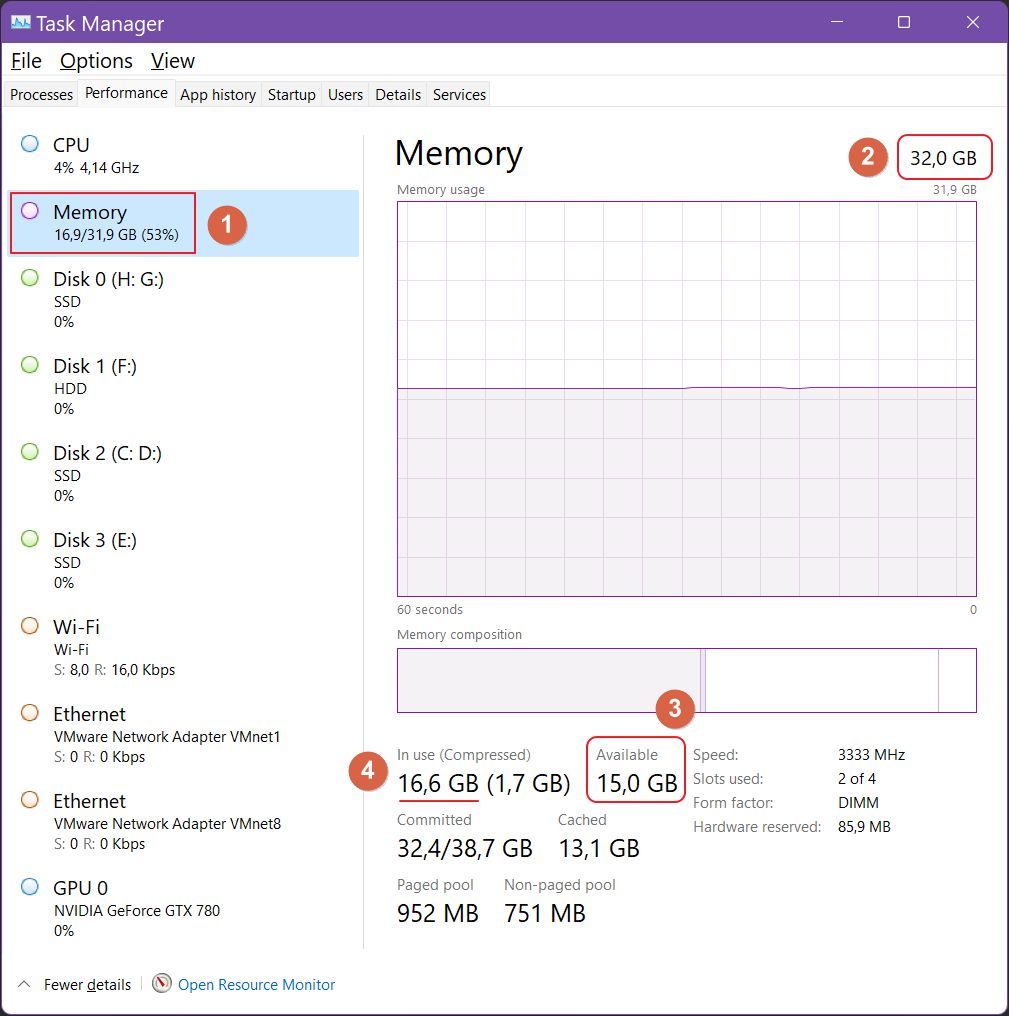
You can see I have 32 GB of RAM installed on my PC. Under these graphs, there’s a ton of info, not just used RAM, but also for compressed amount, cached, speed of RAM in MHz, and so on.
For more RAM details, without having to install another utility, follow this guide.
Check Memory Usage For Each Program in Windows
Knowing how much RAM is available when your computer shows signs of weird slowdowns can’t really solve the problem. You need to know which apps and programs are consuming too much memory.
1. Open the Task Manager app again.
2. Make sure the Processes tab is selected.
3. Click on the Memory header to sort by RAM usage.
The app on top is the worst offender, in this case, my beloved Brave browser. 7 GB of RAM is quite a lot, but I have over 60 tabs open, so it is a bit my fault, to be honest.
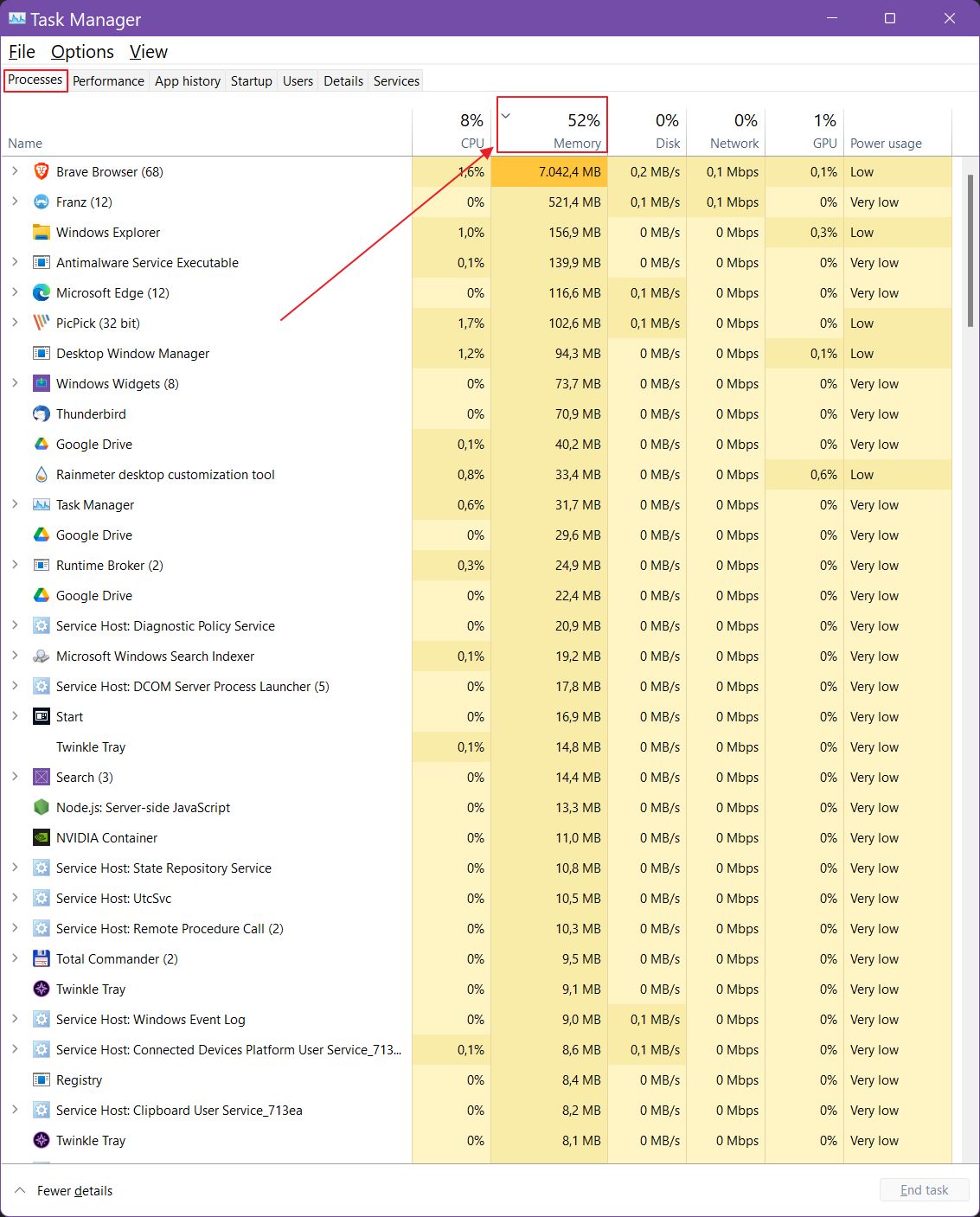
While you’re here you can press the table headers to sort usage by CPU, Disk, Network, GPU, and Power, if you want to see what your programs are doing, which are resource hogs. It can be useful to avoid them in the future.
Note: Windows Resource Monitor is another system utility that can help you dig even deeper into resource consumption for CPU, memory, disk, and network.
Kill a Task That’s Eating Too Much RAM
If you need to kill a program that becomes unresponsive you can do so from the Task Manager. Normally, you would close the app from its menu, but sometimes an app crashes or just hangs and becomes completely unresponsive to user input.
For that, do the following steps:
1. Open the Task Manager app once more.
2. Navigate to the Processes tab.
3. Sort by the Name column, because it will sort running programs alphabetically.
4. Click on the app name. You’ll see a blueish line confirming you have selected the correct program.
5. Click on the End task button and wait for a few seconds for the app to disappear from the processes list. You should see RAM usage dropping immediately.
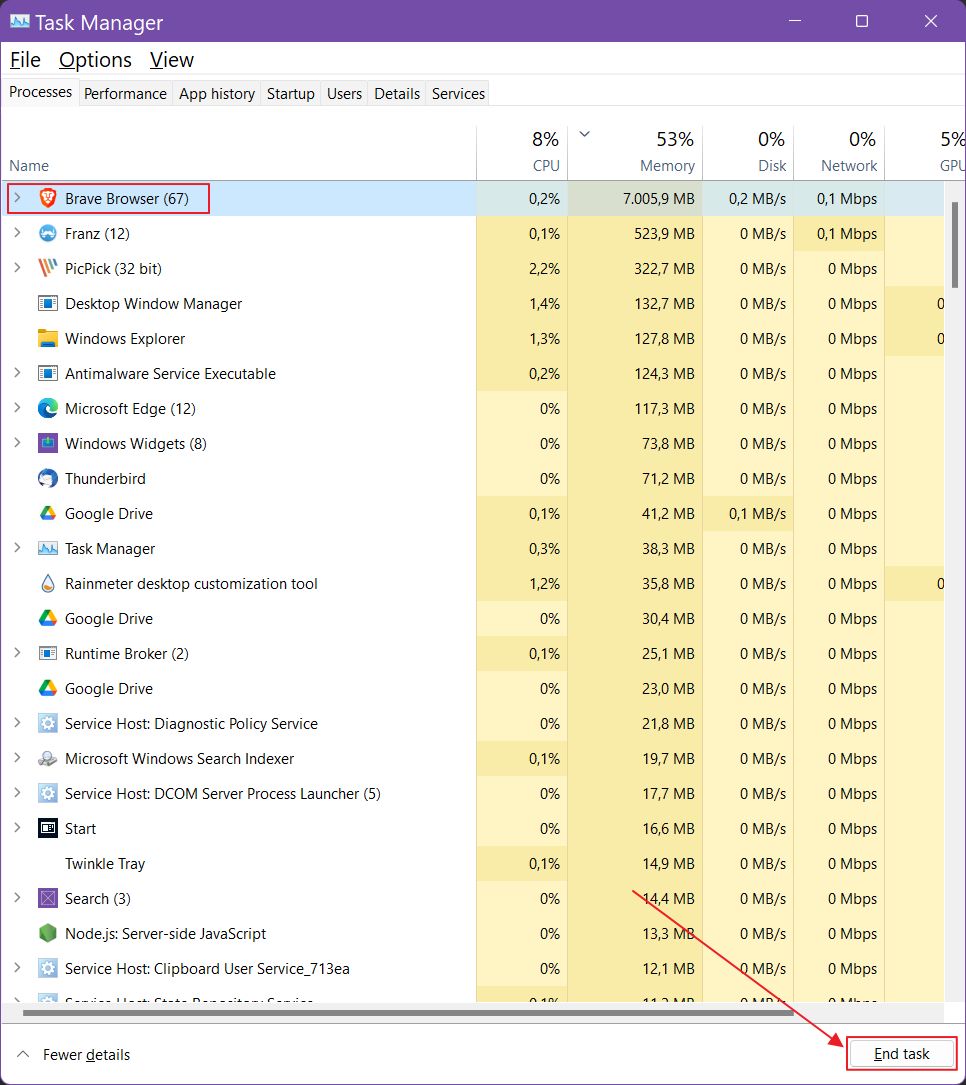
System services suck as the Antimalware Service Executable can’t be stopped from the Task Manager.
Is There Anything You Can Do When Memory Usage is High in Windows?
If you got here hoping for me to tell you some secret shortcuts for what to do when you don’t have enough RAM installed in your system for the apps you’re using I’m afraid I can’t be of much help.
A modern computer would come with at least 8 GB of RAM if you’re just browsing the web and watching movies. For anything else, 16 GB of RAM is just adequate, with 32 GB being what I would call optimal today.
That being said, there are things you can do to lower memory usage in Windows. No guides, just common sense stuff:
- Don’t use too many apps at the same time, especially those that consume too much memory.
- You could explore replacing apps with other equivalents. Try different browsers, photo, and video editors, for example. Some alternatives may be less resource hungry.
- Restart your computer from time to time. This can solve issues caused by closed programs that don’t free up resources on exit.
- If your computer is upgradable and your budget allows, just install more RAM.
Don’t forget to check out our How To Guides section.