- You may have heard about the terms wireless repeaters and wireless bridge when looking for networking devices for your home but you don’t know the difference.
- Learn what a wireless repeater is and how it works.
- Learn what a wireless bridge is and how it works.
- Also, find out when you need to use each type of device and if there’s a better alternative (hint: there is).

When it comes to extending the range of a wireless network, two common options you will find to be very accessible are wireless bridges and wireless repeaters.
As someone who has struggled with poor Wi-Fi signal in the (distant) past, when the 802.11g standard was offering “blistering” speeds, “up to 54 Mbps”, I know firsthand the importance of knowing how to improve wireless signal in your home.
Today we’re going to take a look at two device types that can be used to extend the available usable range of your home network: wireless bridge and wireless repeater. At the end of the article, you’ll also find an alternative that I think it’s worth considering, now that prices dropped into the affordable range.
CONTENTS
What is a Wireless Repeater?
A wireless repeater is a device that can extend the range of a wireless network. The repeater receives wireless signals from a router or access point and then rebroadcasts the amplified signal to extend the effective range of the network.
The connection between the wireless repeater and your main router is wireless. You don’t have to link the two together with a cable.

There’s also one major disadvantage: because the wireless repeater communicates at the same time with the router and a device connected to the repeater node the effective bandwidth is cut in half. So, while a wireless repeater will extend the WiFi coverage of your network with a stronger signal the throughput will suffer for the edge devices that connect via the repeater directly.
Additionally, using multiple repeaters can create a “daisy chain” effect, where each repeater rebroadcasts a weaker signal, which can result in even slower speeds and decreased overall network performance. It’s not common, it depends on how you place these devices, but know it can happen.
Wireless repeaters are useful in situations where a wireless network’s signal is too weak to reach certain areas of the building. They can help eliminate dead zones and improve the overall coverage of a wireless network.
Note: you may find wireless repeaters mislabeled as wireless extenders or wireless boosters. Read the exact specifications to ensure you are getting the device type you actually want.
How Does a Repeater Work?
I think it’s important to first understand how a repeater works.
Wireless repeaters receive the signal from a wireless access point or router and amplify it before retransmitting it. Essentially, these devices extend the range of a wireless network by boosting the existing WiFi signal.
When a wireless signal is transmitted, it loses strength as it travels further from the source. This is known as attenuation. So, a wireless repeater is placed in between the source and the area where the signal is weak, and it boosts the signal so that it can continue to travel further without losing strength.
It’s important to note that a wireless repeater does not create a new WiFi network. Instead, it simply extends the range of an existing network. The extended range will have the same network name (SSID) and security settings as the original network.
When you try to connect to your home network there’s no indication if the current device is connected to the main router or the wireless repeater. It all happens seamlessly from a wireless client point of view.
What is a Wireless Bridge (Media Bridge)?
A wireless bridge is a device that connects two or more network segments together. It allows you to connect devices that are not Wi-Fi enabled, such as TVs, gaming consoles, and Blu-ray players, to your main home network.
The wireless bridge connects to your router or access point using a wireless connection. All devices connect to the wireless bridge via wired connections. The wireless bridge allows these devices to be seen as part of your other network segment, where devices are connected to the main router/access point (with or without wires).
As the name suggests, the wireless bridge creates a bridge between different parts of the same network.

One of the advantages of using a wireless bridge is that it allows you to connect devices that are located far away from your router without having to run Ethernet cables throughout your entire home.
This can be especially useful if you have a home theater setup in a different room from your router or if you have a gaming console that is located in a room that is too far away from your router.
Note: Powerline adapters are an interesting alternative to a wireless bridge or repeater as they use your home electrical grid to bridge two segments of your network.
How Does a Wireless Bridge Work?
A wireless bridge allows me to connect two network segments together through a wireless connection. The bridge works by receiving signals from the primary wireless network and then transmitting those signals to the secondary network devices. And vice-versa.
Remember that all devices that connect to the wireless bridge will use Ethernet cables. The other network segment connects wirelessly directly to the wireless bridge.
This process enables you to extend the network range and connect devices that are physically distant from the primary network.
Wireless bridges are also ideal for connecting devices that do not have a wireless connection or have a weak signal. For example, you can use a wireless bridge to connect a gaming console or a smart TV (known for weak WiFi adapters) to a network that is located in another room.
This is why sometimes the wireless bridge is called a media bridge.
In the corporate environment, wireless bridges are usually used to connect two buildings that are separated by a distance which makes laying a cable impractical. These have very strong signals and can connect to distances much longer than a normal router can cover effectively.
When Do You Use a Wireless Repeater and When Do You Use a Wireless Bridge
As you have already found out: wireless repeaters are not better than wireless bridges. These are two different types of devices with two very different use cases:
- Use a wireless repeater to amplify weak WiFi signals at the edge of your network. Devices connect wirelessly to the repeater.
- Use a wireless bridge to connect two distant segments of your network or to connect legacy devices without a wireless connection to the rest of the network.
Mesh Routers Make Repeaters and Bridges Obsolete
The advent of Mesh WiFi systems makes wireless repeaters, wireless bridges, extenders, and WiFi boosters almost obsolete. I’ve been using an ASUS XT8 Mesh system for a few years now and it works so well that I don’t see the point of ever having to use a bridge or a repeater of any kind.
If I need to extend the range of my network (let’s say I move into a bigger house) all I have to do is buy another ASUS router that supports AiMesh. It doesn’t have to be the same type as my existing routers. In a couple of minutes, I can add the new Mesh node, with no fuss, and no configuring pain.
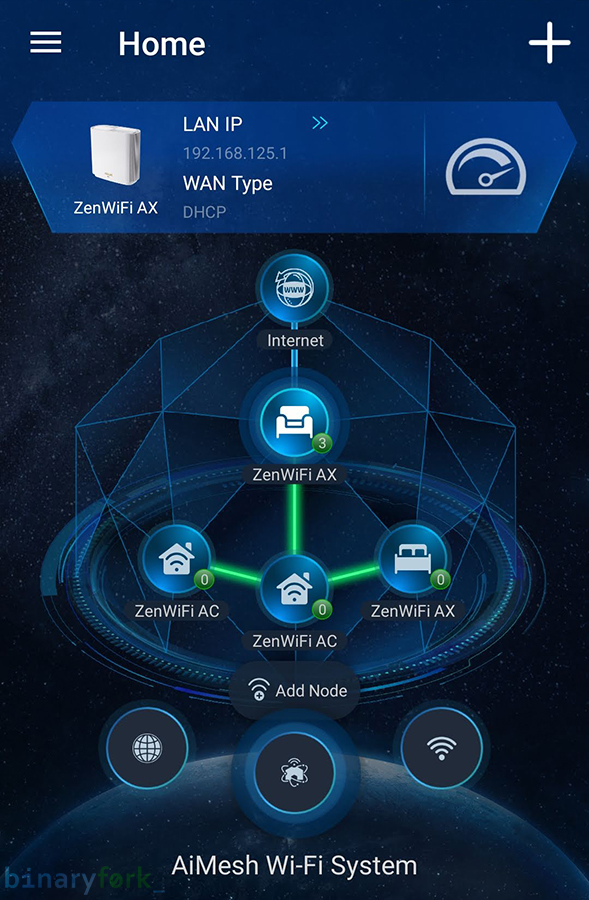
I can connect any device wirelessly to my home network or I can use a short cable to link to the nearest network node. Mesh offers a lot more functionality in my opinion and prices have come down significantly as mass adoption took off.
Sure, Mesh systems are not perfect, but they’re easy to set up and work seamlessly, which is what you want from your home network, a network that will be accessed by your family members and guests.
I’m not saying that specialized Wireless Repeaters and Wireless Bridge devices are not needed anymore, but in home networking, I believe they’re pretty much done.
I’m curious to hear your thoughts on this matter, so don’t hesitate to leave a comment below.