- Your WiFi speed can almost double in certain scenarios if you change just two settings: Throughput Booster and WiFi wireless mode.
- Intel Network Cards offer tons of driver options you can change to improve your wireless speed on your computer or laptop.
- Results will vary depending on your network configuration, but there’s no risk in trying these settings out other than lost time.
Network equipment is hardly what you would call a plug-and-play experience. Sure, there are scenarios where you just turn devices on and connect seamlessly, but if something doesn’t work, or doesn’t function as expected, troubleshooting problems is anything but fun.
In this article, we’re going to see how you can almost double the speed of your Intel Network Card with just a few settings. In some edge cases, like mine, I was able to increase uploads by 7.5x, which is a significant improvement I was able to achieve with just a few clicks and a lot of trial and error.
CONTENTS
Try These Intel WiFi Driver Settings in Windows
Most network cards will use the default Windows driver properties functionality, but you should double-check for other manufacturers if they offer a custom app. Intel drivers don’t need a special app to tap into these advanced settings.
To access Intel WiFi driver settings do the following:
1. Open the Start menu (Win key).
2. Search for Control Panel and open the first result.
3. Click on the View network status and tasks.
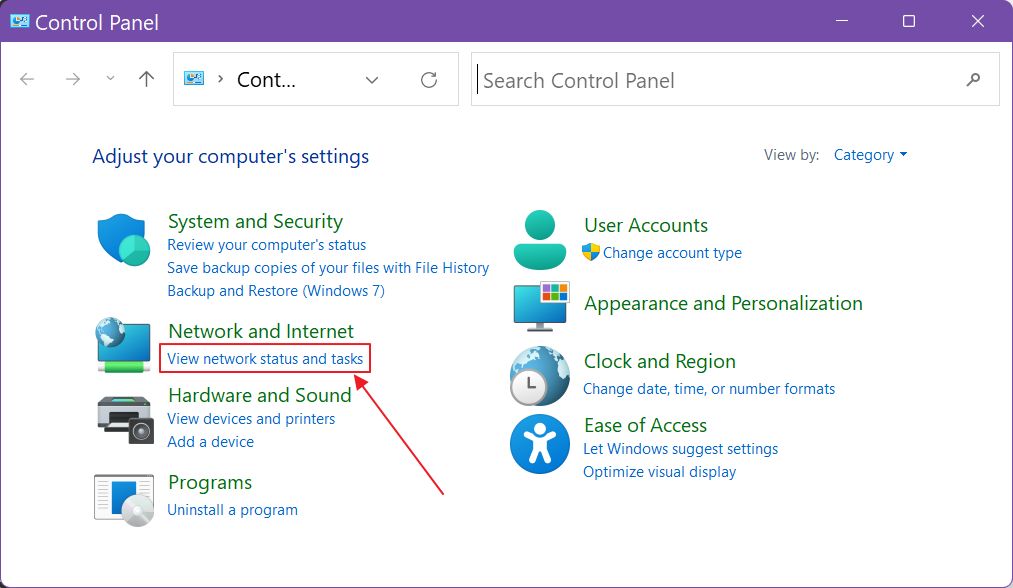
4. On the left side there are a bunch of options. Click on Change adapter settings.
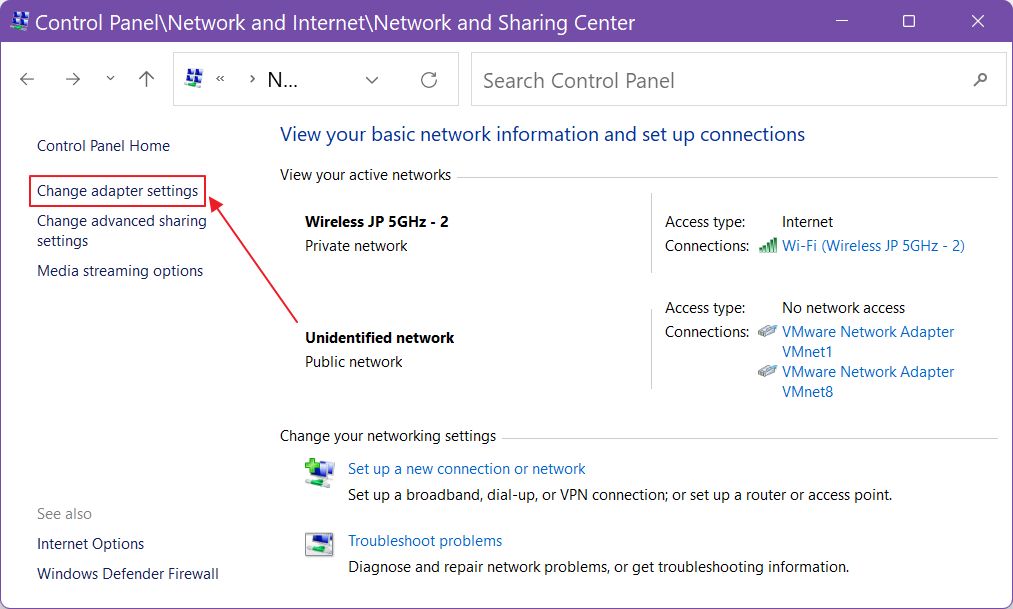
5. A new window will open up. Right-click on the active Intel WiFi card (check the name under its icon) and select Properties.
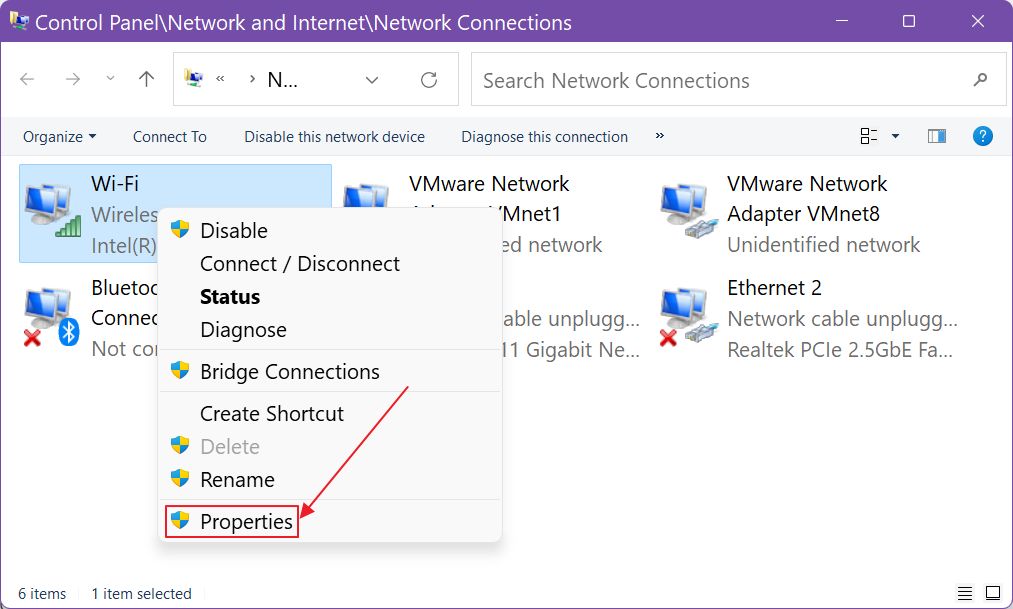
6. A popup window will show up. Click on the Configure button.
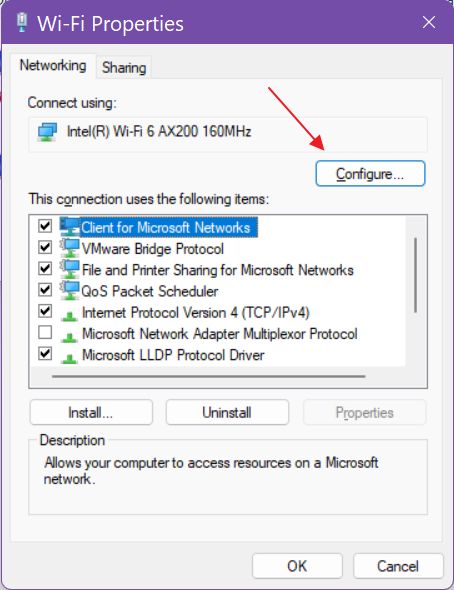
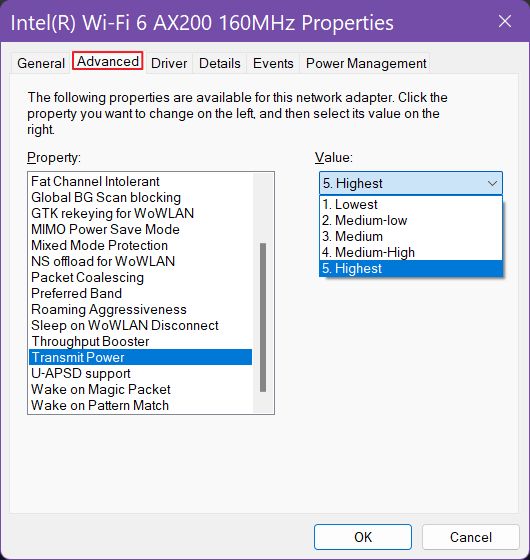
All driver options are found under the Advanced tab (check this Intel official article to understand what each setting does.). There are three options we’re going to talk about in this article:
Transmit Power
This setting changes the transmit power used to send and receive data. The difference is felt in dense areas if you choose a higher level, where multiple radio signals collide. Higher transmit power levels should reduce interference.
This setting will affect battery life in laptops, but if you’re looking for speed just select level 5. Highest for best performance.
WiFi Throughput Booster
Wondering what is throughput booster and what does throughput booster do? This setting will improve upload speed from client to access point/router and you’ll mostly feel the difference when you’re sending large files.
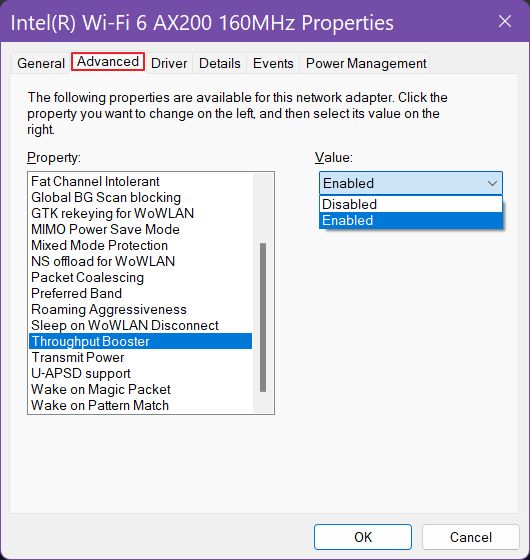
Should you keep the throughput booster On or Off? The answer is not that simple, as with all the settings in this article. I think you should test your speed, enable the setting, test again, then decide based on the results you get on your particular setup.
Change Intel WiFi Card Wireless Mode (Can Help With Compatibility)
I was obsessed for a long time with the topic of this article for a simple reason: my Intel AX200 WiFi 6 card upload speed was capped at only 229 Mbps for uploads, while downloads were fine at over 2400 Mbps. It drove me nuts.
I was able to replicate the problem with another identical card installed on a laptop. The problem persisted with Windows 10 and Windows 11, on multiple driver versions and router firmware. It had to do with my ASUS mesh system and the only solution I found was to change the Wireless Mode to AC (WiFi 5).
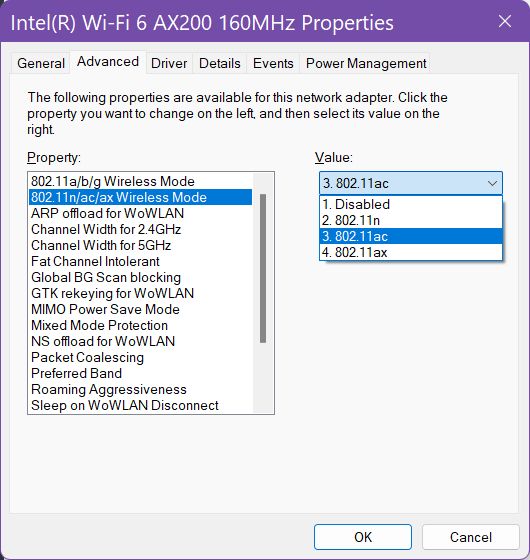
This downgraded the download speed to 1733 Mbps but also increased the upload link from 229 Mbps to a whooping 1733 Mbps. That’s more than a 7.5x increase.
I wouldn’t say this setting has changed my life, but it definitely solved my problem for good. Hope it helps you too if you’re facing the same problem, even if it sounds counterintuitive to downgrade your connection to increase its speed.
Network connections always involve two devices, so make sure that your router is also configured properly: enable and connect to a 5 GHz or 6 GHz SSID, and also make sure WiFi 6 (AX) mode is enabled if your router supports it.
If there’s a router or NIC firmware update, make sure you’re using the latest version on both. Also, always install the latest drivers.
Intel has an article you should read detailing the optimal settings for 802.1ax (WiFi 6) connectivity.
Check WiFi Link Speed in Windows
I recommend you do two more things after changing any of these settings. Check the link speed, as reported by Windows, then do your own tests.
Verify Reported Link Speed in Windows 10 and Windows 11
1. Open the Network Connections window again (search in the Start Menu or use the guide from the beginning of the article).
2. Right-click on the active WiFi connection and select Status.
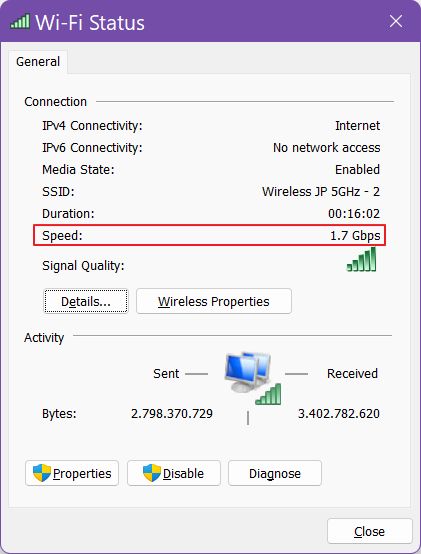
3. In the new popup window look for Speed. The number you see is the minimum between upload and download speed.
Check Download and Upload Link Speed in Windows 11
In Windows 11 it’s possible to get more details on the link speed, but you’ll have to use the Settings app.
1. Open the Settings app by searching in the Start menu directly.
2. Select the Network & internet tab from the left-side menu.
3. Scroll inside the right-side panel until you reach Advanced network settings. Click to open.
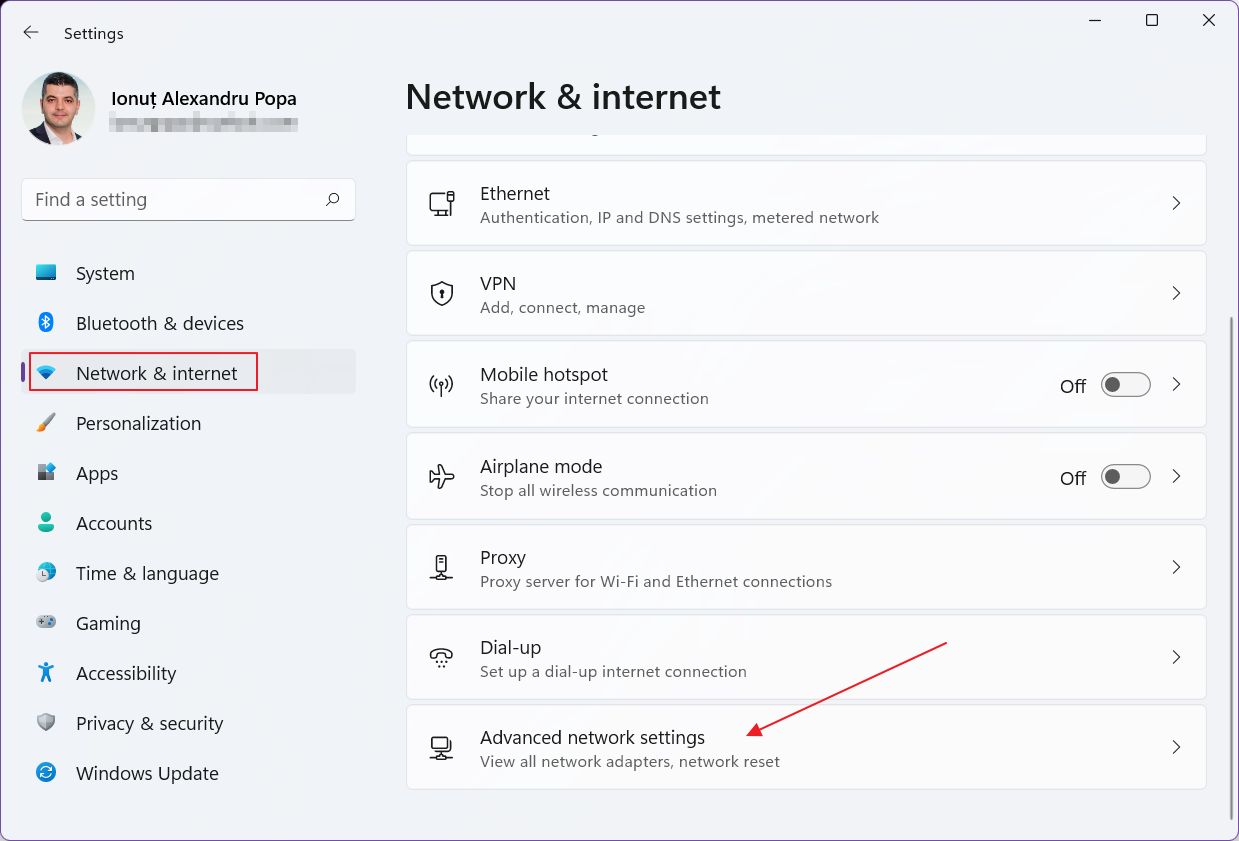
4. At the top of the new page you’ll see listed all NICs installed on your PC. Expand the Intel WiFi connection by clicking on the down arrow.
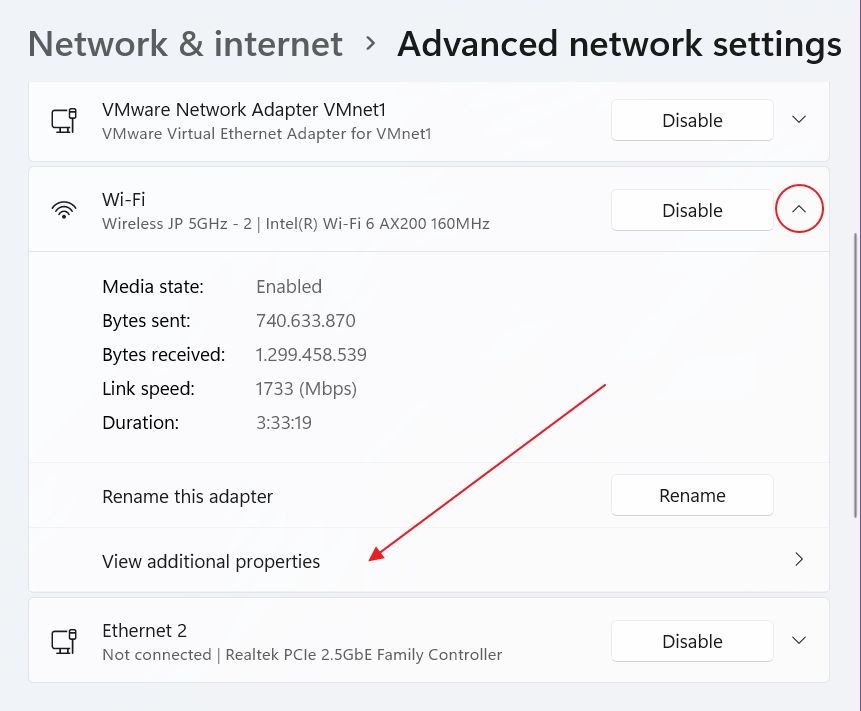
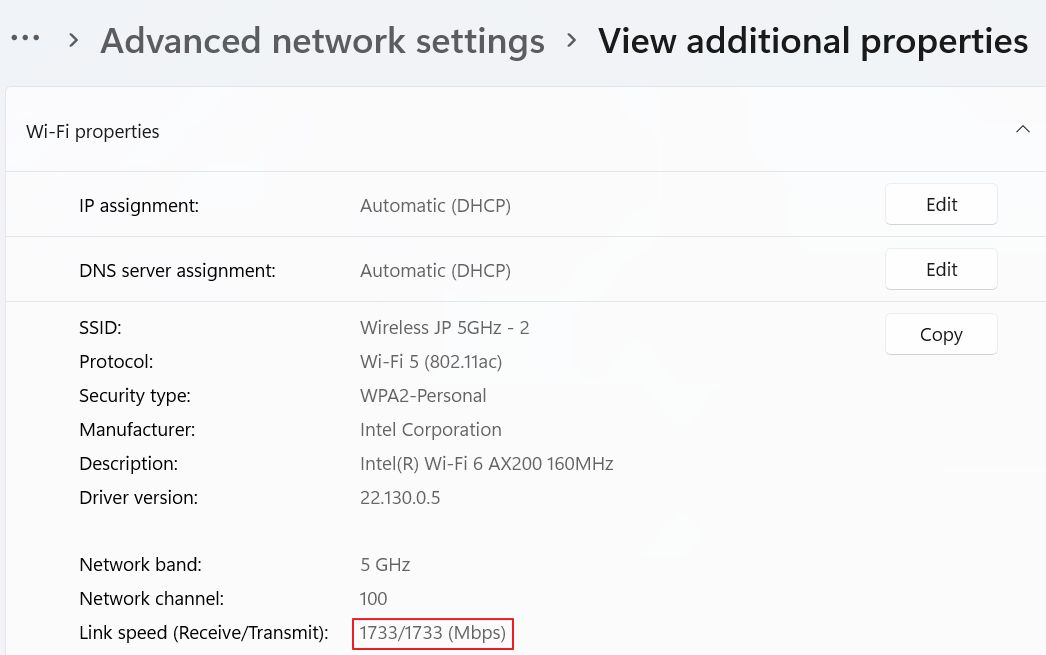
5. Click on View additional properties.
6. Scroll and check Link speed (Receive/Transmit). Receive is the download speed, while transmit is the upload speed.
Speed Tests: Check What Works Best for Your Configuration
All these changes have to be put to the test. I’m always using SpeedTest.Net because it’s easy to compare results between multiple runs. Alternatively you can use our free tool to test your Internet speed.
Here’s the result with Throughput Booster disabled and Transmit power on Level 1:
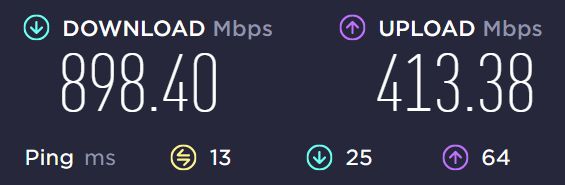
Here’s the result with Throughput Booster disabled and Transmit power on Level 5:
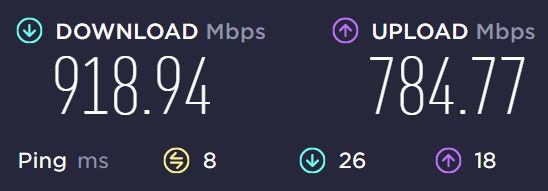
This change alone almost doubled the upload speed. That’s a significant improvement. The download only improved by a little.
And the final result with Throughput Booster enabled and Transmit power on Level 5:
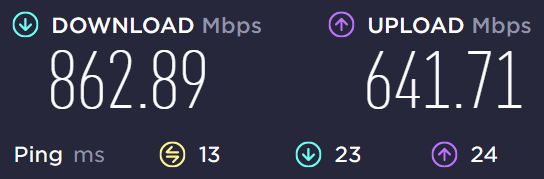
It’s clear that in my case Throughput Booster doesn’t help much. So I’ve disabled the option, kept the Transmit power to level 5, and downgraded the link speed to WiFi 5, which turned out to be the most important change.
For comparison here are the results directly from my ASUS router admin interface, on a 1 Gbps wire connection. The test was performed with SpeedTest too.
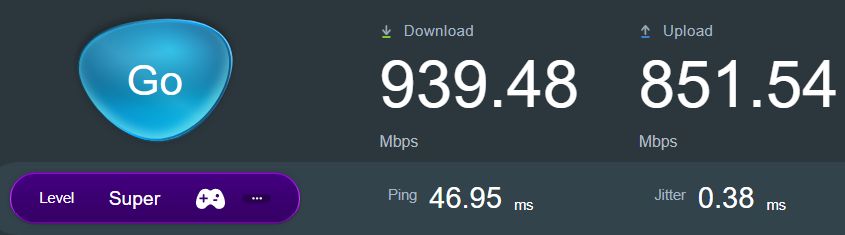
Now let’s turn to your experience. What settings did you find to greatly improve your Intel network card speed from stock settings?
Also read: how to boost WiFi signal and speed.