- Windows System Restore also referred to as System Protection, is a backup and restore utility for important system files.
- System Restore is baked right into Windows, but it’s not enabled by default.
- System Restore creates restore points automatically (or manually) and is able to recover your Windows installation to a previous working state.

Once you get to know Windows you’ll find tons of utilities that help safeguard and restore your important data. One of the central apps for keeping your Windows system integrity in check is System Restore, also known as System Protection.
Keep reading to find out what does System Restore do, how it works, and how best you can take advantage of it. I’ve included links to separate System Protection guides where appropriate.
Check the dedicated section for more details about Windows Backup and Restore utilities.
CONTENTS
What is System Restore?
System Restore is the Windows feature that controls the creation and restoration of important system files through Restore Points.
If System Restore is enabled on your computer it will create Restore Points automatically when certain actions are performed.
You can also create manual restore points whenever you feel like you’re going to do something that might break your system. It’s actually recommended to do so.
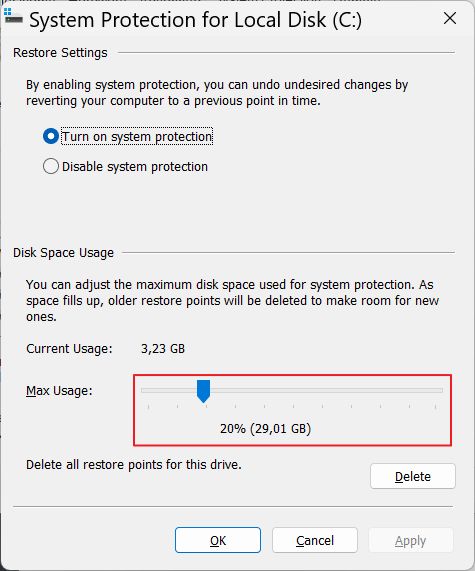
Older Restore Points are automatically deleted when a certain percentage of your drives is filled. You can control how much space System Restore is allowed to use for each of your computer drives and partitions.
Related guides:
- How to Turn On System Protection (includes how to allocate space for Restore Points).
- How to Turn Off System Protection, which is not recommended, but possible.
- How to Delete All Restore Points at Once to Free Up Space on your drive.
When Does System Restore Create a Restore Point Automatically?
If System Protection is enabled on your Windows PC, an automatic Restore Point is created every time you:
- Install software
- Update hardware drivers
- Install new hardware drivers
Manual Restore Points can also be created when needed. We also have a guide for creating manual Restore Points.
Is Windows System Protection the Same Thing as System Restore?
Confusingly, depending on where you find yourself in Windows settings you’ll see either a mention of System Restore or a mention of System Protection.
System Restore and System Protection are the same thing. It’s a bit unintuitive, but now you know there’s no difference between these two.
What Does System Restore Do?
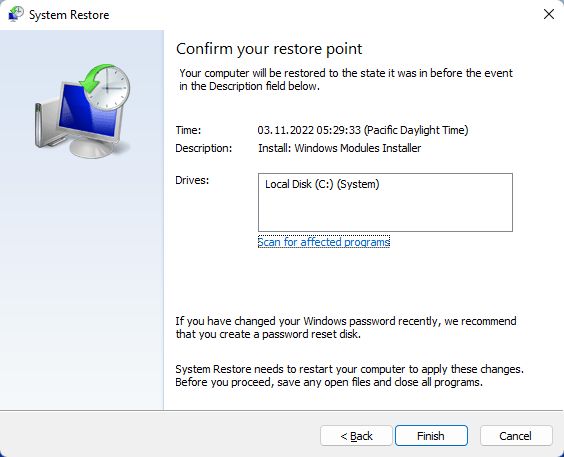
When System Restore creates a Restore Point it will make a backup, called snapshot, of important system files and the entire Windows Registry database.
In case of a failure or data corruption, you can use Restore Points to get your system up and running, even if the PC fails to boot.
Related guides:
- How to revert to a Specific Restore Point Directly from Windows.
- How to revert to a working Restore Point From the Recovery Environment.
- How Long Does System Restore Take to revert to a previous Restore Point? We timed the action for both Windows 10 and Windows 11.
What System Restore Doesn’t Do?
It’s important to remember that a System Restore Point will not include your personal files, the ones saved in the user Documents folder.
If you need to save user documents you can save user files with the Windows Backup and Restore utility, then restore personal files as needed, when needed.

What is Windows Recovery Environment and How to Launch It
I hope this article answers the most basic questions about System Restore / System Protection. Make sure you follow the links for specific step-by-step guides.